Laser Modules South America are vital components in numerous applications across industries ranging from medical devices to telecommunications. These small yet powerful devices emit focused light beams and are used in a variety of ways, including optical communication, barcode scanners, medical equipment, and more. In this article, we’ll explore what laser modules are, how they work, and the different types available.
What Are Laser Modules?
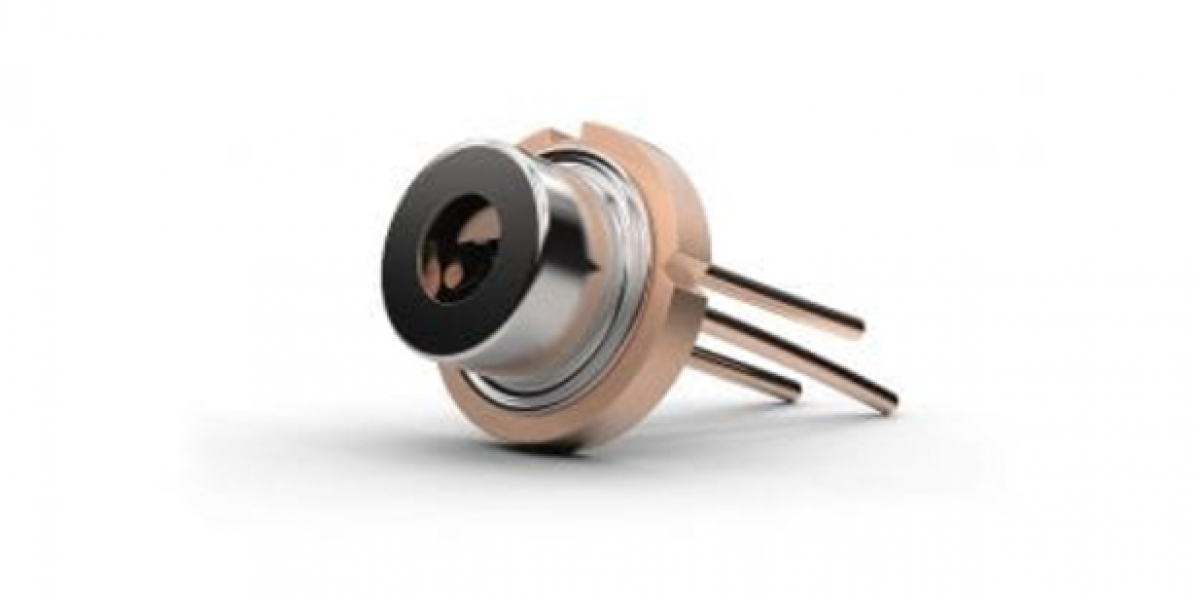
A laser module is a compact and self-contained unit that generates a coherent beam of light through a process called stimulated emission of radiation. The module houses several key components, including a laser diode (the source of the light), a lens (to focus the beam), and a driver circuit (to regulate power and ensure the laser operates safely).
Laser modules vary in terms of size, power output, wavelength, and the type of laser they use. These factors determine the applications they are best suited for. Whether for industrial, medical, or consumer use, laser modules play a significant role in modern technology.
How Do Laser Modules Work?
At the core of any laser module is the laser diode, which is responsible for generating light. When an electric current is passed through the diode, electrons in the semiconductor material become excited and release photons as they return to their lower energy states. These photons bounce between mirrors, stimulating further photon emission, which creates a coherent light beam.
The emitted light passes through an optical system that focuses or collimates the beam to meet specific requirements. The driver circuit ensures the module operates at optimal power levels and protects it from overheating or electrical damage.
Types of Laser Modules
Laser modules come in several types, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Some common types include:
Diode Laser Modules: These are the most common type of laser module. They are compact, efficient, and typically have a low power consumption. Diode lasers are widely used in laser pointers, barcode scanners, and printers.
Fiber Laser Modules: These lasers use optical fibers to amplify the light generated by the laser source. Fiber lasers offer high power, efficiency, and beam quality, making them ideal for industrial applications like metal cutting, welding, and material processing.
CO2 Laser Modules: These lasers use carbon dioxide gas as the lasing medium. They are commonly used in engraving, cutting, and marking materials like wood, plastics, and metals. CO2 lasers are favored for their ability to produce high-power output with a relatively large beam size.
DPSS Laser Modules: Diode-pumped solid-state lasers (DPSS) use a diode laser to pump a solid-state material, such as Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet), to produce light. These lasers are used in applications requiring high precision, such as in medical treatments and laser spectroscopy.
UV Laser Modules: These lasers produce ultraviolet light, which is particularly useful for applications requiring high precision and the ability to interact with materials at the microscopic level. UV lasers are used in applications like semiconductor lithography and microfabrication.
Applications of Laser Modules
Laser modules are versatile tools with a broad range of applications. Here are some of the key industries where they are used:
Telecommunications: Laser modules are integral to fiber-optic communication systems, where they transmit data over long distances through optical fibers. They are used to convert electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa.
Medical: In the medical field, laser modules are used for a wide range of treatments and procedures, including laser surgery, eye surgeries (such as LASIK), and diagnostic equipment like laser scanners.
Industrial: Laser modules are extensively used for material processing, including cutting, engraving, welding, and marking. High-power lasers are often used in manufacturing processes to improve precision and efficiency.
Consumer Electronics: Laser modules are widely used in consumer electronics, such as optical disc drives (CD, DVD, Blu-ray), laser pointers, and barcode scanners. They provide an efficient means of data reading and transmitting.
Aerospace and Defense: Laser modules are used in various defense and aerospace applications, such as in rangefinders, target designation, and LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) systems.
Advantages of Laser Modules
Compact and Efficient: Laser modules are small and highly efficient, making them suitable for integration into compact devices.
Precision: Laser beams are extremely precise, allowing for accurate measurements, cutting, and engraving in industrial and scientific applications.
Durability: Laser modules are designed to be robust, with many capable of operating in harsh environments and under challenging conditions.
Versatility: Laser modules can be used in a wide array of applications across different industries, making them highly versatile.
Choosing the Right Laser Module
When selecting a laser module, several factors should be considered:
Wavelength: The wavelength of the laser determines the type of material it interacts with. For instance, longer wavelengths (like infrared) are used for materials like metal, while shorter wavelengths (like ultraviolet) are suitable for delicate processes.
Power Output: The power of the laser module affects its range and the material it can process. Higher power is typically needed for industrial applications such as cutting or welding.
Size and Form Factor: Depending on the application, the size of the laser module may be a critical factor, especially in compact or portable devices.
Cost: Depending on the technology and performance, laser modules can vary significantly in price, so it’s important to balance cost with the required specifications.
Conclusion
Laser modules are powerful and versatile components that play a crucial role in modern technology. From industrial manufacturing to medical procedures, these devices are integral to countless applications. As technology continues to evolve, laser modules will likely become even more advanced, opening up new possibilities in a wide range of industries.
If you're considering using a laser module in your next project, understanding the various types, applications, and factors to consider will help you choose the best solution for your needs. Whether you're working on a cutting-edge medical device or a consumer gadget, laser modules offer exceptional precision, efficiency, and versatility.