In the modern world, managing water runoff and preventing flooding is a critical challenge for urban areas, residential communities, and industrial sectors alike. One of the most effective ways to address this issue is through the installation of underground drainage systems and a well-designed storm drainage system. These systems not only protect property and infrastructure from water damage but also play a vital role in maintaining public health and environmental sustainability.
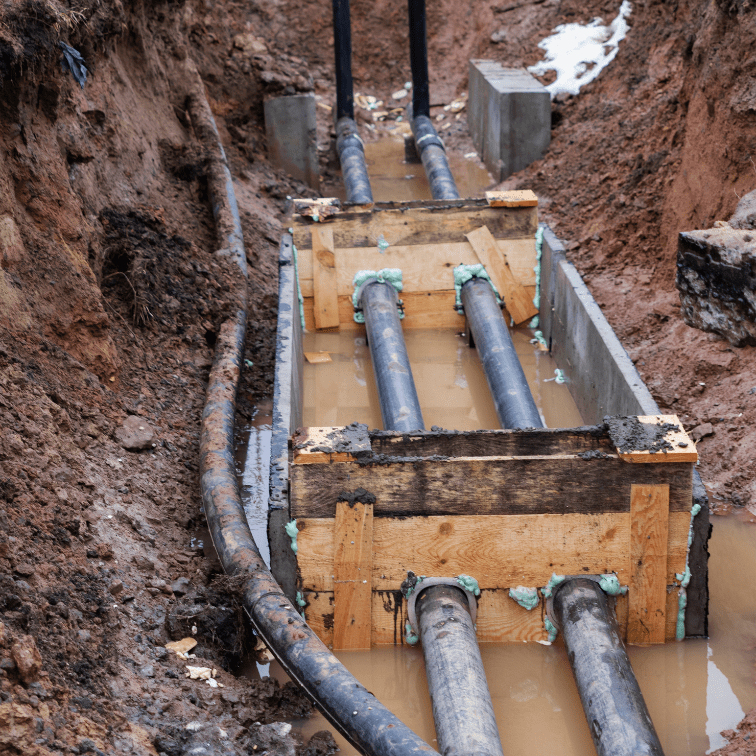

What Are Underground Drainage Systems?
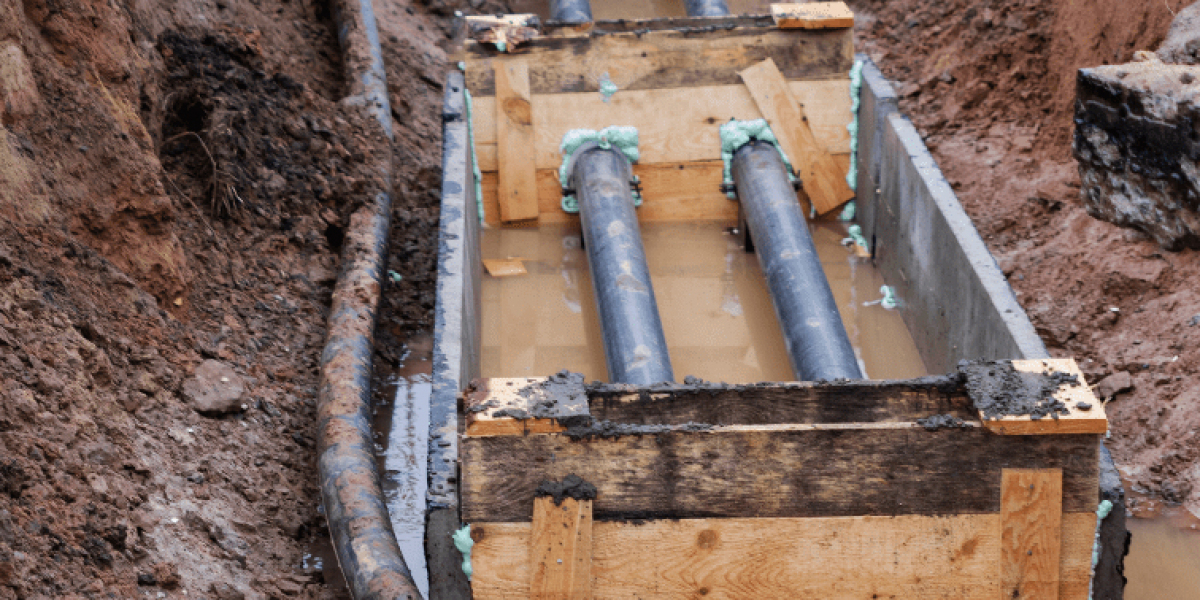
Underground drainage systems are engineered networks designed to carry away excess water from streets, properties, and agricultural lands. These systems typically consist of pipes, channels, and culverts that are buried below the ground surface, directing water flow to safe disposal locations such as treatment facilities or natural water bodies.
The primary purpose of underground drainage systems is to prevent surface flooding caused by heavy rainfall or poor water absorption. By channeling water through subterranean pipes, these systems keep roads, homes, and businesses dry while reducing the risk of structural damage and erosion.
Key Benefits of Underground Drainage Systems
- Flood Prevention: A well-designed underground drainage system ensures that water is efficiently diverted away from vulnerable areas, reducing the likelihood of floods that could damage buildings or roads.
- Aesthetic and Safety Advantages: Because these systems are buried beneath the ground, they eliminate the need for visible ditches or trenches, improving the visual appeal of a neighborhood or industrial area. They also make the space safer by removing potential hazards that open drainage systems might pose.
- Improved Hygiene and Health: Underground drainage systems help manage wastewater and stormwater, which is crucial for maintaining sanitary conditions and preventing the spread of waterborne diseases.
What Is a Storm Drainage System?
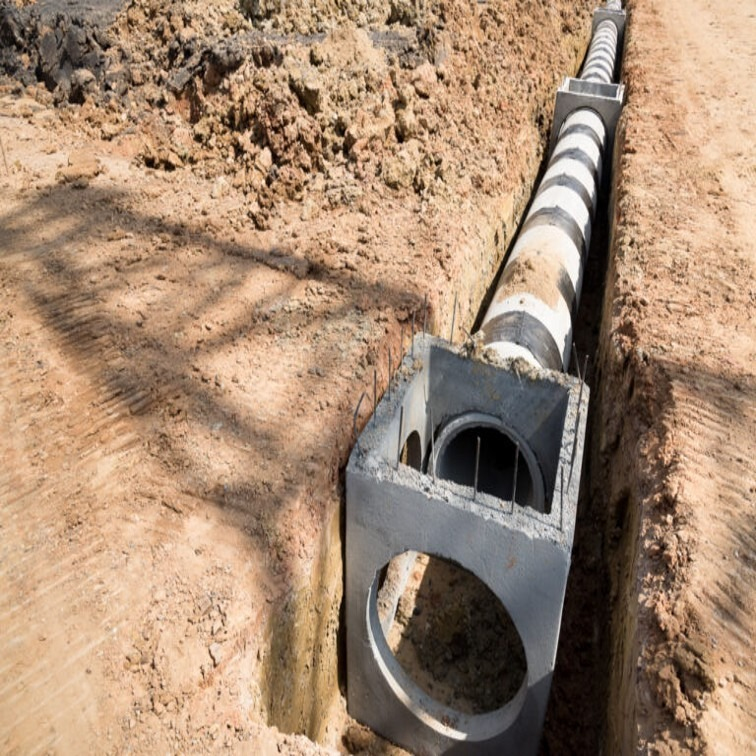
A storm drainage system is a specialized network that helps manage surface runoff caused by rainstorms. Unlike traditional sewage systems, storm drainage systems are designed specifically to handle large volumes of rainwater quickly and efficiently. These systems consist of catch basins, storm drains, and underground pipes that direct water into larger systems or natural water bodies like rivers or lakes.
The goal of a storm drainage system is to prevent urban flooding, protect natural ecosystems from erosion, and minimize the environmental impact of runoff, which may carry pollutants into water sources.

Conclusion
Effective water management is crucial for the growth and sustainability of modern communities, and underground drainage systems and storm drainage systems play an essential role in this effort. By preventing flooding, protecting infrastructure, and safeguarding public health, these systems provide a foundation for a safer and more resilient environment. Whether you’re looking to install a new drainage system or improve an existing one, it’s important to understand the key principles and best practices involved in designing and maintaining these systems.