1. Introduction to Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
In today’s digital landscape, cyber threats are evolving rapidly, creating the need for robust systems to assess and manage risks. A Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment (TVRA) is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and addressing the vulnerabilities within an organization’s infrastructure. This process helps companies understand potential threats, pinpoint weak points, and determine the risk levels associated with those vulnerabilities.
1.1 Understanding the Basics: What Is Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment?
At its core, a threat vulnerability risk assessment evaluates potential risks to assets, especially sensitive data, to protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks. This assessment goes beyond identifying the threats themselves; it analyzes how these threats exploit existing weaknesses, thus helping organizations prioritize and mitigate these risks effectively.
1.2 Importance of Conducting Risk Assessments for Cybersecurity
Risk assessments play a vital role in building a robust security posture. With proactive assessments, companies can anticipate threats and minimize their impact on business operations. Regular assessments offer an up-to-date view of the risk landscape, allowing organizations to adapt security measures and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
2. Key Components of Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
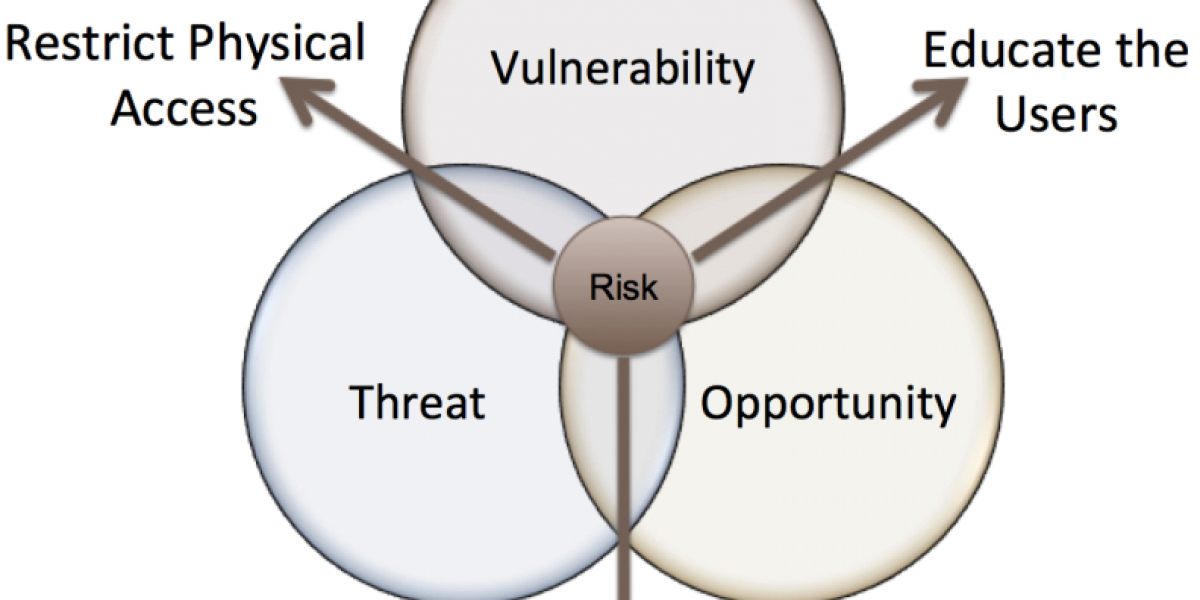
A thorough threat vulnerability risk assessment encompasses three main components: threats, vulnerabilities, and risks. Understanding each component helps security teams design effective strategies to safeguard systems.
2.1 Defining Threats: Types and Examples
Threats are potential events or actions that could harm an organization’s data or systems. They can be classified as:
- External Threats: Hacking, phishing, or DDoS attacks from outside the organization.
- Internal Threats: Insider threats from employees, whether accidental or intentional.
- Natural Threats: Natural disasters, such as earthquakes or floods, that could disrupt infrastructure.
2.2 Vulnerabilities: Identifying Weak Points in Systems
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses within a system that threat actors can exploit. These include outdated software, weak passwords, and unpatched security flaws. Identifying these vulnerabilities is essential for mitigating potential damage.
2.3 Risks: How Threats and Vulnerabilities Combine to Form Risks
When a threat exploits a vulnerability, it creates a risk. Risks represent the potential for loss or damage. Assessing risk levels helps organizations allocate resources effectively to mitigate the most significant threats.
3. Steps in Conducting a Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
A structured approach is crucial for a successful assessment. These steps ensure that each aspect of risk assessment is thoroughly examined and addressed.
3.1 Risk Identification and Analysis
Risk identification begins with recognizing potential threats and vulnerabilities within the organization’s infrastructure. Tools like vulnerability scanners can highlight areas that need attention, while risk analysis involves understanding the potential impact of each identified risk.
3.2 Risk Evaluation and Prioritization
Once risks are identified, they must be evaluated based on their potential impact and likelihood. Organizations often use risk matrices or scoring systems to rank risks, allowing them to prioritize their security efforts efficiently.
3.3 Risk Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation involves deploying controls and strategies to reduce or eliminate risks. These strategies include implementing firewalls, encryption, access control, and employee training programs to reinforce security from various angles.
4. Tools and Techniques for Effective Risk Assessment
A variety of tools and techniques enhance the effectiveness of threat vulnerability risk assessments. These tools support continuous monitoring and in-depth analysis.
4.1 Common Tools Used in Risk Assessment
Some commonly used tools include:
- Vulnerability Scanners: Automatically detect system weaknesses.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Centralize and analyze security data from various sources.
4.2 Techniques for Identifying and Analyzing Threats
Techniques like penetration testing, scenario analysis, and data flow mapping allow security teams to assess potential attack vectors and simulate real-world threat scenarios.
5. Common Challenges in Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
Despite the value of TVRA, organizations face challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. Addressing these issues requires a strategic approach.
5.1 Overcoming Data Collection Barriers
Data collection can be complex, especially when information is dispersed across departments. Using centralized tools can help streamline data collection and ensure consistency.
5.2 Dealing with False Positives and False Negatives
Risk assessment tools can sometimes produce inaccurate results. False positives may flag non-threatening activities as threats, while false negatives may miss actual risks. Ensuring regular tool updates and using a layered security approach can minimize these inaccuracies.
5.3 Ensuring Comprehensive Coverage of Threats and Vulnerabilities
Covering all possible threats and vulnerabilities can be difficult, particularly for large organizations. Implementing routine assessments and engaging third-party experts for audits can enhance coverage.
6. Best Practices for Effective Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
To optimize risk assessments, certain best practices can enhance the thoroughness and accuracy of the results.
6.1 Regular Updates and Assessments
Threat landscapes evolve, and organizations must conduct assessments regularly. Consistent updates to software, policies, and procedures are crucial for staying ahead of new threats.
6.2 Utilizing a Layered Approach to Cybersecurity
A layered approach combines multiple security measures, such as antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection, which together provide more robust protection than any single method.
7. Real-World Examples of Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessments
Case studies showcase how risk assessments can benefit various sectors and highlight best practices for risk management.
7.1 Case Study 1: Successful Risk Mitigation in a Finance Sector Organization
A major financial institution employed a multi-layered risk assessment strategy to protect customer data, highlighting the importance of continuous monitoring and rapid incident response.
7.2 Case Study 2: Risk Management in the Healthcare Sector
A hospital implemented rigorous risk assessments to safeguard patient information, demonstrating the role of compliance in risk mitigation within sensitive industries.
8. Future Trends in Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the methods and tools for conducting TVRA will also advance.
8.1 Emerging Threats in Cybersecurity
New threats, such as AI-driven attacks, require updated assessment techniques. Understanding these emerging threats helps organizations prepare proactively.
8.2 Technological Advances in Risk Assessment Tools
Innovations like machine learning and artificial intelligence enhance risk assessment tools, enabling them to analyze larger datasets and make more accurate predictions.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
9.1 What Is a Threat Vulnerability Risk Assessment?
TVRA is the process of identifying and analyzing potential security threats, vulnerabilities, and associated risks within an organization.
9.2 How Often Should Companies Conduct Risk Assessments?
Most companies conduct assessments at least annually, although high-risk industries may require more frequent evaluations.
9.3 What Are the Costs Associated with Risk Assessment?
Costs vary depending on the organization’s size, complexity, and the tools used, but it’s essential to weigh these against the potential costs of data breaches.
9.4 What’s the Difference Between a Threat and a Vulnerability?
A threat is an external or internal force that could cause harm, while a vulnerability is a weakness that makes it possible for threats to exploit.
9.5 How Does Risk Assessment Benefit Small Businesses?
Risk assessments help small businesses protect their assets with limited resources by identifying and addressing critical security gaps.
9.6 Can Risk Assessments Prevent All Cybersecurity Threats?
No, but they can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of attacks by proactively identifying and mitigating risks.
10. Conclusion: Enhancing Security Through Proactive Assessment
Conducting a threat vulnerability risk assessment is essential for any organization looking to safeguard its assets and data. By proactively identifying and mitigating risks, organizations can enhance their resilience against cyber threats, maintain customer trust, and uphold regulatory compliance.