The digital age has fundamentally transformed how young people connect and communicate. While technology provides remarkable opportunities for interaction, it also presents challenges in developing vital social skills. The youth mental health crisis, intensified by the pandemic and the growing use of social media, highlights the necessity of nurturing meaningful connections both online and offline.
This article aims to explore the complexities of the digital divide and its effects on youth mental health. We will examine the significance of offline social skills, the obstacles that arise from digital communication, and practical strategies to bridge this gap.
By the end of this article, you will gain insights into fostering a balanced approach to social interaction that not only supports youth mental health but also enhances overall emotional well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The digital divide significantly affects the development of student social skills, impacting youth mental health.
- Offline interactions are crucial for emotional health, resilience, and forming genuine connections.
- Bridging the gap requires proactive strategies from parents, educators, and communities to support student wellness.
Understanding the Digital Divide and Its Impact on Youth Mental Health
The term "digital divide" refers to the gap between individuals who have access to digital technology and those who do not. This gap is particularly pronounced among young people, as their socialization increasingly occurs through screens.
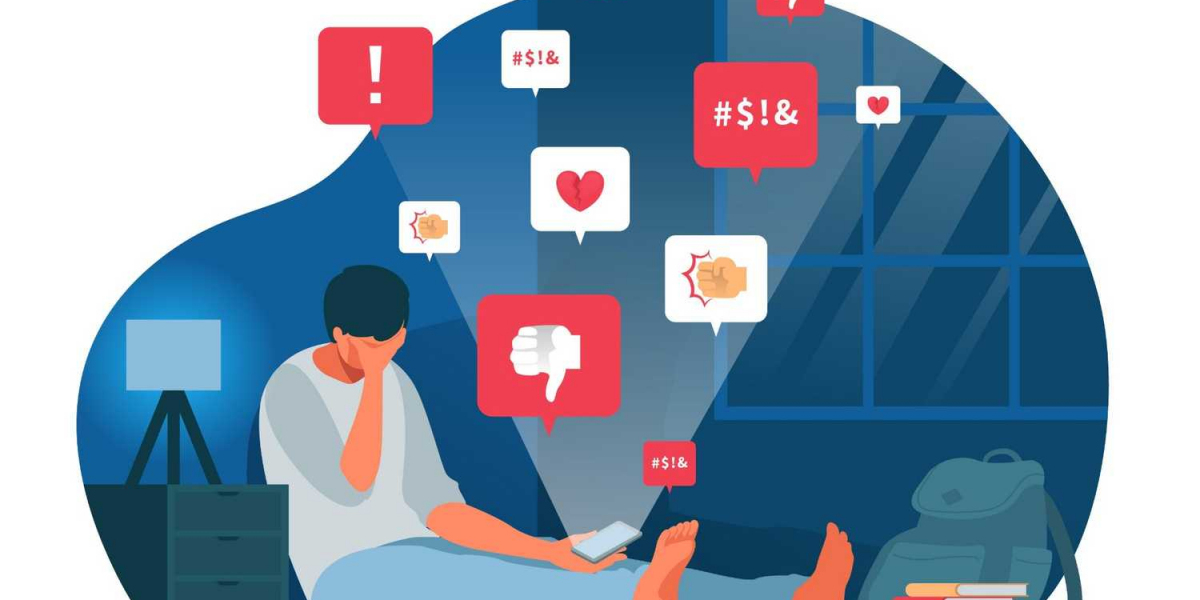
While technology facilitates communication and socialization, it can also impede the development of crucial face-to-face interactions.
For many young people, the consequences of this divide can be profound, particularly concerning emotional health and student mental health.
The youth mental health crisis is marked by rising levels of anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation, making it essential to examine how digital communication shapes these experiences.
The Importance of Offline Social Skills
Why Offline Interaction Matters?
In a world dominated by screens, the value of offline social skills cannot be overstated. Offline interactions provide opportunities for young people to learn essential skills such as empathy, active listening, and conflict resolution. These skills are vital for building emotional resilience and navigating life's challenges.
Building Emotional Wellness Through Face-to-Face Communication
Research shows that offline interactions promote emotional wellness by fostering genuine connections. Young people who engage in face-to-face communication report higher levels of satisfaction and lower instances of feelings of isolation.
The nuances of body language, tone, and facial expressions enrich these interactions, which are often lost in digital communication.
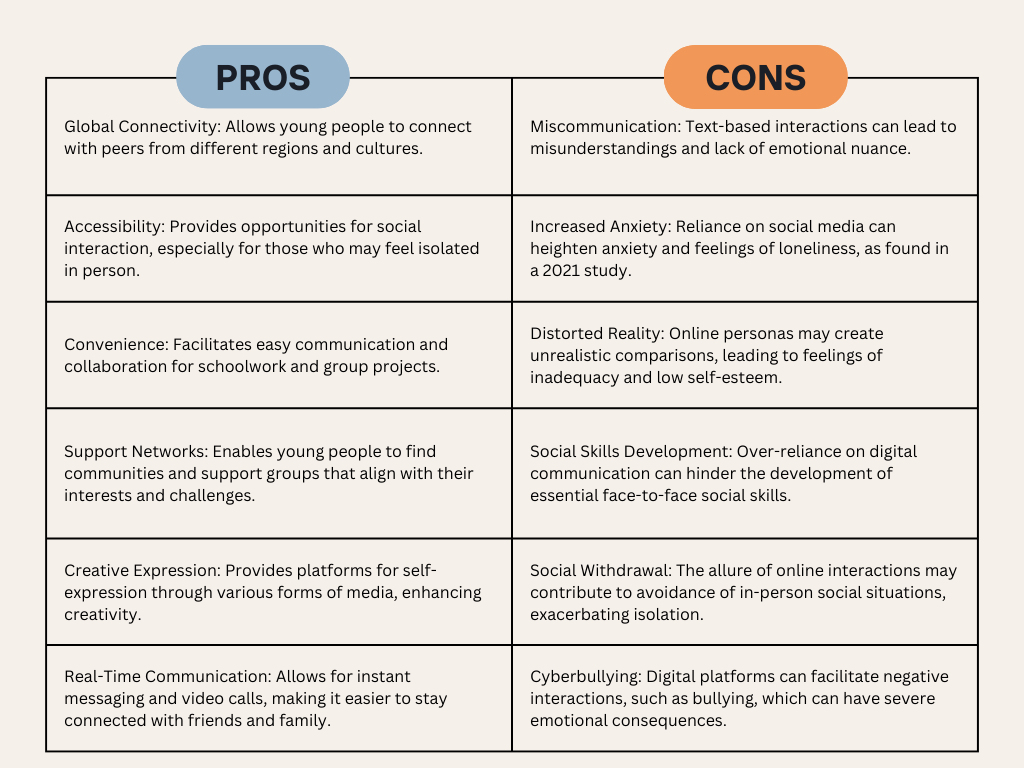
Pros and Cons of Digital Communication
Bridging the Gap: Strategies for Fostering Offline Social Skills
Creating Opportunities for In-Person Interaction
To combat the negative effects of the digital divide, it is essential to create opportunities for young people to engage in offline activities.
Schools, families, and communities can play a vital role by promoting social events, extracurricular activities, and volunteer opportunities that encourage face-to-face interactions.
Schools could organize team-building activities, outdoor adventures, or community service projects that require collaboration and communication.
Such experiences allow students to develop their social skills in real-world settings, which can bolster their emotional health and resilience.
Promoting Emotional Health Education
Education systems should integrate emotional health education into the curriculum. Teaching students about emotional wellness, empathy, and conflict resolution can help them develop the skills needed to navigate social situations both online and offline.
Incorporating lessons on mental health awareness can also equip students with the knowledge to recognize when they or their peers are struggling.
This understanding can foster a supportive school environment where students feel comfortable seeking help or offering support to others.
The Role of Parents and Educators
Encouraging Balanced Technology Use
Parents and educators can guide young people in developing healthy technology habits. Setting boundaries around screen time and encouraging breaks from devices can foster more opportunities for offline interactions.
Family activities such as game nights, nature outings, or community events can create a supportive environment for young people to practice their social skills.
Parents should also model positive behavior by limiting their own device use during family interactions, emphasizing the importance of being present.
Modeling Positive Social Behavior
Adults play a critical role in shaping young people's social skills. By modeling effective communication and emotional health practices, parents and educators can demonstrate the importance of balancing digital and offline interactions.
Teachers can incorporate collaborative learning activities in the classroom, allowing students to work together in person. This hands-on approach fosters a sense of community and belonging, which is crucial for emotional wellness.
Building Community Support Systems
Engaging Community Resources
Communities can help bridge the digital divide by providing resources and programs that encourage in-person connections.
Local organizations can host events focused on fostering emotional wellness and social skills, allowing young people to practice these essential abilities.
Youth centers can offer workshops on communication skills, conflict resolution, and teamwork. These programs can provide young people with the tools they need to navigate social interactions successfully.
Utilizing Mental Health Support Services
Access to mental health care is crucial for young people navigating the complexities of the digital divide. Schools and communities should prioritize mental health resources to support students experiencing mental health crises and help them develop coping strategies for their emotional health challenges.
School counselors should be trained to recognize signs of mental health problems and provide appropriate support. Additionally, collaboration with mental health organizations can ensure that students have access to the care they need.
Conclusion
The time for action is now. Schools, families, and communities must collaborate to support student social skills and mental health. By doing so, we can ensure that young people develop the emotional resilience and social competencies they need to navigate life successfully.
While technology continues to evolve, our commitment to fostering healthy social connections must remain a priority. Through proactive strategies and a supportive environment, we can help young people bridge the digital divide and enhance their overall wellness.
This commitment is not just beneficial; it is essential for nurturing emotionally healthy, socially skilled young people who can face the complexities of life with confidence and resilience.