In the world of regenerative medicine, amniotic membrane transplants have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, offering significant benefits across various medical fields. The amniotic membrane, derived from the innermost layer of the placenta, is packed with nutrients, growth factors, and bioactive molecules that promote tissue regeneration and healing. This membrane has been successfully used in many areas of modern surgery, from ophthalmology to wound care, making it a versatile and invaluable tool for surgeons and patients alike.
What Are Amniotic Membrane Transplants?
Amniotic membrane transplants involve the use of tissue from the amniotic membrane, which surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. This membrane is rich in collagen, growth factors, and anti-inflammatory proteins, making it ideal for healing and regeneration. The tissue is ethically sourced from placentas donated after childbirth, with consent from the mother. After thorough screening and processing, the membrane can be used in a variety of medical procedures, either as a graft or in sheet form to cover wounds and surgical areas.
1. Accelerating Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration
One of the most remarkable properties of amniotic membrane transplants is their ability to significantly accelerate wound healing. The membrane contains a variety of bioactive molecules, such as growth factors and cytokines, which are essential for tissue repair. When applied to a wound or surgical site, the membrane creates an optimal environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration.
In wound care, amniotic membrane transplants are often used to treat chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and burns. These types of wounds are notorious for being slow to heal, often leading to complications if not properly managed. The application of an amniotic membrane graft can drastically reduce healing time, decrease the risk of infection, and improve overall patient outcomes.
Clinical Application:
In chronic wound treatment, amniotic membrane transplants have demonstrated their ability to regenerate damaged tissue, reduce scarring, and enhance recovery. Patients who have struggled with long-term wounds now have access to a more effective solution that promotes faster healing.
2. Reducing Inflammation and Pain
Inflammation is a natural response to injury, but excessive or chronic inflammation can hinder the healing process and lead to pain. One of the key benefits of amniotic membrane transplants is their anti-inflammatory properties. The membrane contains molecules that actively reduce inflammation, creating a more favorable environment for healing and reducing the associated pain.
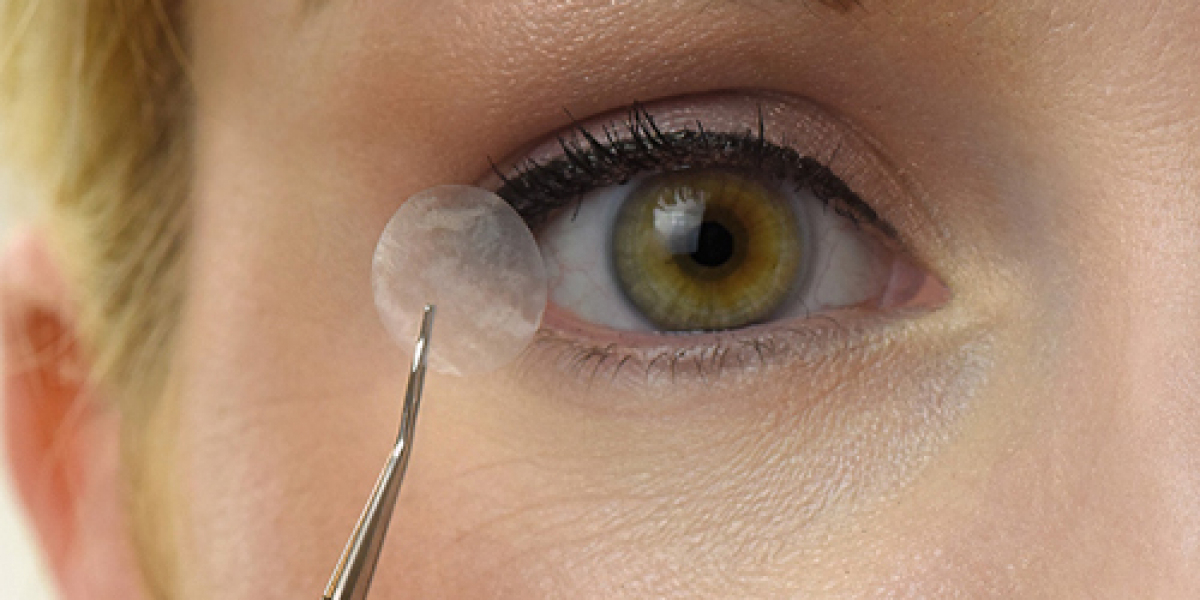
In many surgical applications, such as orthopedic and ophthalmic surgeries, amniotic membrane transplants have been used to minimize inflammation and provide relief to patients. By reducing inflammation, the risk of complications is also lowered, allowing patients to recover more comfortably and quickly.
Clinical Application:
In ophthalmology, amniotic membrane transplants are used in surgeries to treat conditions like corneal ulcers and conjunctival defects. The membrane not only helps heal the affected area but also reduces post-surgical inflammation, leading to quicker recovery times and less discomfort for patients.
3. Decreased Risk of Infection
One of the major concerns in surgery is the risk of infection, which can complicate recovery and lead to additional medical interventions. Amniotic membrane transplants have natural antimicrobial properties, which help prevent infections at the surgical site or wound area. These properties, combined with the anti-inflammatory effects, create an environment where harmful bacteria are less likely to thrive.
This is especially beneficial in cases where patients are at a higher risk of infection, such as those with compromised immune systems or individuals recovering from major surgeries. The antimicrobial qualities of amniotic membrane transplants provide an added layer of protection, ensuring that the healing process can proceed without complications.
Clinical Application:
In surgical settings, amniotic membrane transplants are often used to cover wounds and incisions, particularly in patients who are more susceptible to infections. These grafts not only promote healing but also act as a barrier against bacteria, reducing the need for antibiotics or additional treatments.
4. Minimizing Scarring
Another benefit of amniotic membrane transplants is their ability to minimize scarring. Scar tissue forms as the body heals, but excessive scarring can cause long-term discomfort, limited mobility, and aesthetic concerns. The unique composition of the amniotic membrane, which includes collagen and growth factors, encourages the formation of healthy tissue rather than scar tissue.
By promoting more efficient cell regeneration, amniotic membrane transplants reduce the likelihood of developing thick, unsightly scars. This is particularly important in surgeries that involve visible areas, such as the face, or in procedures where flexibility and mobility are critical, such as in joint surgeries.
Clinical Application:
Plastic surgeons have begun incorporating amniotic membrane transplants into procedures like skin grafts and reconstructive surgeries to minimize scarring. This not only improves the cosmetic outcome for patients but also ensures a more functional recovery, especially in areas requiring flexibility.
5. Versatility Across Multiple Medical Fields
The versatility of amniotic membrane transplants is perhaps one of their most compelling features. These grafts can be used in a variety of medical specialties, including ophthalmology, orthopedics, dermatology, and plastic surgery. Whether applied to the skin, corneas, or soft tissues, the membrane adapts to the specific needs of the tissue it is repairing, making it a highly flexible and adaptable tool.
In ophthalmology, amniotic membrane transplants have become the standard for treating corneal defects and other ocular surface disorders. In orthopedics, they are used to promote healing in tendon and ligament injuries. The ability to use this membrane in such a wide range of medical fields highlights its potential to revolutionize patient care across the board.
Clinical Application:
In orthopedic surgeries, amniotic membrane transplants are used to aid the healing of damaged tendons and ligaments. Surgeons often use the membrane as a protective covering over surgical repairs to encourage faster healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
The power of amniotic membrane transplants lies in their regenerative, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties, making them an indispensable tool in modern surgery. From wound care to ophthalmology, these grafts are transforming the way patients heal and recover. Their ability to accelerate healing, reduce scarring, and minimize the risk of infection ensures that patients experience better outcomes, less pain, and faster recoveries.
As the field of regenerative medicine continues to evolve, amniotic membrane transplants will likely play an even larger role in shaping the future of surgery. For patients and surgeons alike, this innovative treatment offers a safer, more efficient, and more natural approach to healing.