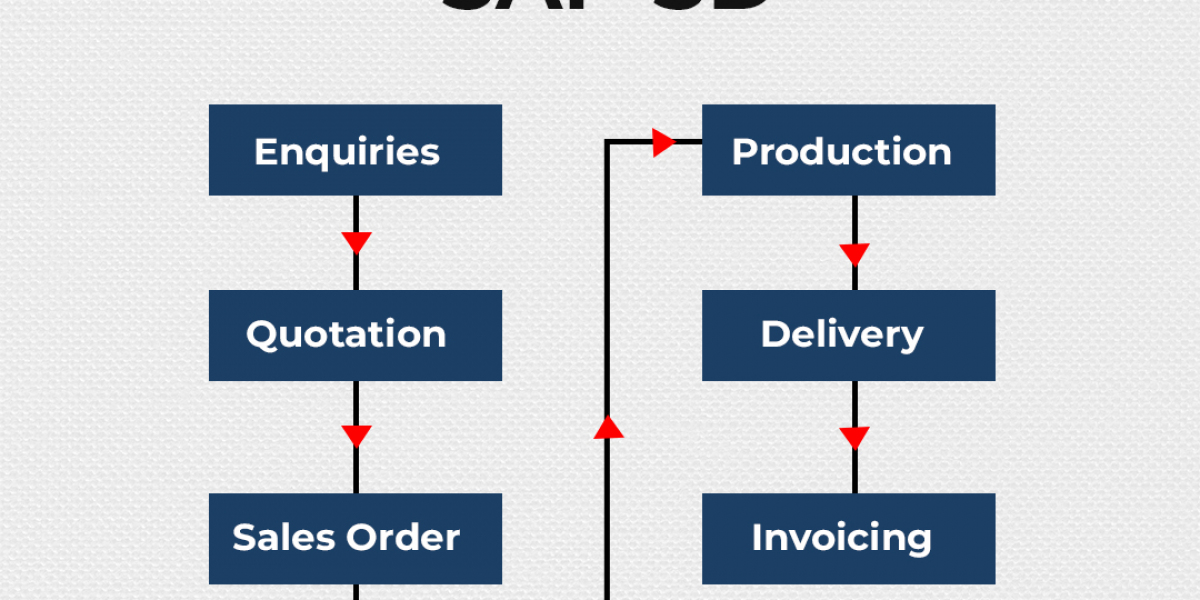
SAP SD is a vital module in the dynamic realm of ERP. Its purpose is to oversee sales procedures, such as order fulfillment, inventory control, and client billing. Anyone hoping to develop in this sector must comprehend the fundamentals of the SAP SD course offered by prestigious institutions. We'll go over the main components of the SAP SD syllabus in this blog post and how they work together to create a thorough education.
Introduction to SAP SD
SAP SD is a module within the SAP ERP system that handles sales and distribution activities. It's crucial for managing sales orders, shipping, billing, and invoicing, making it an integral part of any organization's supply chain management. The SAP SD syllabus covers a wide range of topics to equip learners with the necessary skills to effectively manage and optimize these processes. Top institutes offering SAP SD training ensure their syllabus is up-to-date and aligns with industry standards, providing students with relevant knowledge and practical skills.
1. Master Data Management
One of the foundational elements of the SAP SD syllabus is Master Data Management. This component focuses on the creation and management of key data types, including customer master data, material master data, and pricing conditions.
- Customer Master Data: This includes detailed information about customers, such as contact details, credit limits, and payment terms. Effective management of this data is crucial for maintaining strong customer relationships and ensuring accurate order processing.
- Material Master Data: This pertains to the products or services offered by the company. It includes data such as product descriptions, prices, and stock levels.
- Pricing Conditions: This involves setting up and managing pricing structures, discounts, and surcharges. It ensures that the pricing strategy aligns with the company's financial goals and market conditions.
Master Data Management is critical as it forms the backbone of all sales and distribution processes. Proper understanding and handling of this data are essential for the smooth functioning of the SAP SD module.
2. Sales Order Management
Sales Order Management is another crucial component of the SAP SD syllabus. This section covers the complete lifecycle of a sales order, from creation to delivery and billing.
- Order Creation: This involves entering sales orders into the SAP system. It includes selecting the customer, specifying the products or services, and determining the delivery and payment terms.
- Order Processing: This includes tracking the status of orders, managing changes, and handling any issues that arise during the process.
- Delivery Processing: This component deals with the logistics of shipping the products to the customer. It includes picking, packing, and shipping the goods.
- Billing: This involves generating invoices and processing payments. It ensures that all financial transactions related to the sales order are accurately recorded.
Mastery of Sales Order Management is vital for ensuring efficient and accurate order fulfillment, which directly impacts customer satisfaction and business performance.
3. Credit Management and Risk Assessment
Credit Management and Risk Assessment is an essential part of the SAP SD syllabus that deals with evaluating and managing credit risk associated with sales transactions.
- Credit Limits: Setting and monitoring credit limits for customers helps mitigate financial risk and ensures that sales are conducted within the company’s risk tolerance.
- Risk Assessment: This involves assessing the creditworthiness of customers based on their payment history and financial stability. It helps in making informed decisions about extending credit and managing accounts receivable.
- Credit Checks: Performing credit checks during the order processing stage ensures that sales are made only to customers who meet the company’s credit criteria.
Understanding and managing credit risk is crucial for maintaining financial stability and minimizing potential losses due to non-payment.
4. Integration with Other SAP Modules
The integration of SAP SD with other SAP modules is another core component of the syllabus. SAP SD doesn’t operate in isolation; it interacts with various other modules within the SAP system.
- Integration with SAP MM (Materials Management): This integration ensures that the inventory levels are updated in real-time as sales orders are processed and deliveries are made.
- Integration with SAP FI (Financial Accounting): This ensures that all financial transactions related to sales orders are accurately recorded in the financial system, including invoicing and payments.
- Integration with SAP PP (Production Planning): This allows for coordination between sales orders and production planning, ensuring that production schedules align with sales demands.
Understanding these integrations is crucial for ensuring that the SAP SD module functions smoothly within the broader SAP ecosystem.
Conclusion
The SAP SD syllabus is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the sales and distribution processes within an organization. By covering essential components such as Master Data Management, Sales Order Management, Credit Management, and Integration with other SAP modules, top institutes ensure that learners are well-equipped to handle the complexities of SAP SD.