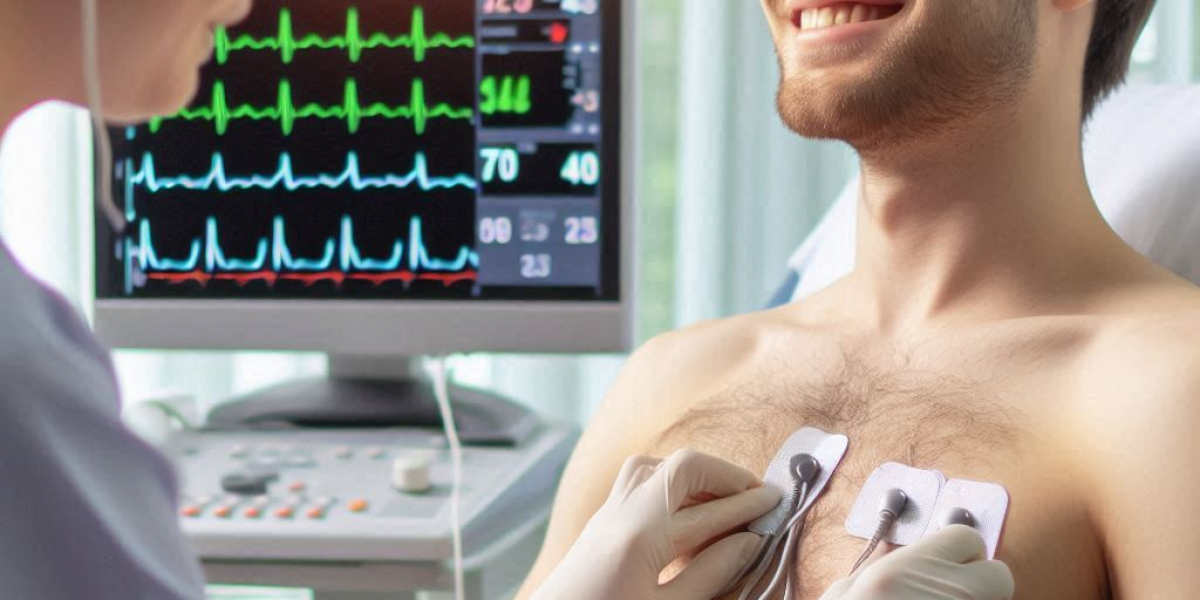
In the world of modern medicine, various diagnostic tools help doctors evaluate a patient's heart health. One such vital tool is the ECG Test, a non-invasive and widely used procedure to assess the heart's electrical activity. Understanding what an ECG is, how it works, and when it’s necessary can help patients be more informed and prepared for their healthcare journey.
What is an ECG Test?
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) test records the electrical signals produced by your heart. Every time your heart beats, it creates an electrical impulse that travels through your heart. This electrical activity can be measured by electrodes attached to your skin, and the result is displayed as a graph with different wave patterns. The test helps doctors see how well your heart is functioning.
The ECG test measures several critical aspects of heart activity, such as:
- Heart rate: How fast your heart is beating.
- Heart rhythm: The regularity of the heartbeats.
- Electrical conduction: How well electrical impulses travel through the heart.
The results from the test provide important insights into any underlying heart conditions, whether minor or severe, allowing timely interventions if necessary.
How Does the ECG Work?
The ECG is a simple procedure that involves attaching small electrode patches to the skin on the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes are connected to a machine that records the heart’s electrical activity. The test usually takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
Step-by-Step Process:
- Preparation: The technician will ask you to lie down. Your chest area may be cleaned, and in some cases, hair might need to be shaved to ensure better contact with the electrodes.
- Placing the Electrodes: The technician will place 10 electrodes on your body—typically on the arms, legs, and chest.
- Recording the Heart Activity: Once the electrodes are in place, the machine records the electrical impulses of your heart. You will be asked to stay still and breathe normally during the recording to avoid interference.
- Reading the Results: The test results are displayed on the monitor as a graph or printed out on paper. The doctor will examine these wave patterns to determine if there are any abnormalities.
Why is an ECG Test Performed?
There are several reasons why your doctor may recommend an ECG test. It can be used for both preventive screening and diagnosis.
Common Reasons for an ECG:
- Chest pain: If you experience sudden or ongoing chest pain, your doctor might order an ECG to determine whether it’s related to heart problems.
- Shortness of breath: If you have difficulty breathing, it could be linked to heart issues, and an ECG can help pinpoint the cause.
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia): If your heart feels like it's fluttering, skipping beats, or pounding, an ECG can assess the electrical activity and diagnose the problem.
- Heart disease screening: For those with a family history of heart disease or other risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, or smoking, an ECG can help detect any early signs of heart trouble.
- Check heart health after a procedure: After heart surgery, a heart attack, or other major treatments, an ECG is often used to monitor recovery.
Types of ECG Tests
There are different variations of the ECG test, depending on what the doctor needs to assess.
Resting ECG
This is the most common type of ECG. It records the heart's activity while the patient is lying still. It helps detect problems with the heart’s rhythm and size of the chambers.
Stress ECG (Exercise ECG)
In this type of ECG, the patient is asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal on a stationary bike while the ECG records how the heart functions under physical stress. It is often used to diagnose coronary artery disease.
Holter Monitoring
For this test, you wear a portable ECG device for 24 to 48 hours. It continuously records your heart’s activity, allowing the doctor to detect any irregularities that may not occur during a short, regular ECG.
Event Monitoring
Event monitors are worn for a longer period, usually for weeks or even months. They are designed to capture specific irregularities that happen occasionally.
What Can an ECG Test Diagnose?
The ECG Test is incredibly useful in diagnosing a variety of heart-related conditions, such as:
Heart Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats. They can be too fast, too slow, or erratic. The ECG can detect these anomalies and help identify the type of arrhythmia.
Coronary Artery Disease
This condition occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. An ECG can reveal signs of restricted blood flow to the heart, often during a stress test.
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
An ECG can show if you've had a heart attack in the past or if one is currently happening. The test records changes in the electrical patterns that may occur during a heart attack.
Cardiomyopathy
This is a condition where the heart's muscles are abnormal, which can be detected by the changes in the electrical activity in an ECG.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Electrolytes like potassium and calcium are essential for proper heart function. An imbalance in these electrolytes can affect the heart’s electrical activity, which can be identified through an ECG.
Is an ECG Test Safe?
The ECG is a completely safe and non-invasive procedure. There are no risks involved since it doesn't send electricity into the body; it only measures the electrical signals that naturally occur.
Preparing for the Test
There isn’t much preparation needed for an ECG. You can eat and drink normally before the test. However, avoid applying lotions or oils to the skin before the test, as they can interfere with electrode placement.
Limitations of the ECG Test
Although an ECG is a valuable tool, it does have its limitations. It only provides a snapshot of the heart's electrical activity at the time the test is conducted. If you have intermittent symptoms or issues that don’t occur frequently, like occasional chest pain or arrhythmia, a regular ECG may not capture these abnormalities.
For those cases, your doctor might recommend more comprehensive tests such as Holter monitoring or a stress test to get more detailed results.
An ECG Test is an essential tool for diagnosing and monitoring heart health. It helps detect various heart conditions early on, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. With its simplicity, safety, and efficiency, the ECG continues to be a cornerstone of cardiac care in modern medicine. Understanding the test's importance, procedure, and potential diagnoses can help patients make informed decisions about their heart health and well-being.