How Long Does It Take For Celexa To Get Out Of Your System? Understanding the duration of Celexa remains in your system is crucial for managing medication transitions and side effects. This guide explores the factors influencing Celexa's clearance from your body, ensuring you have the insights needed for a smooth and informed process. Let's unravel the timeline together.
About Celexa
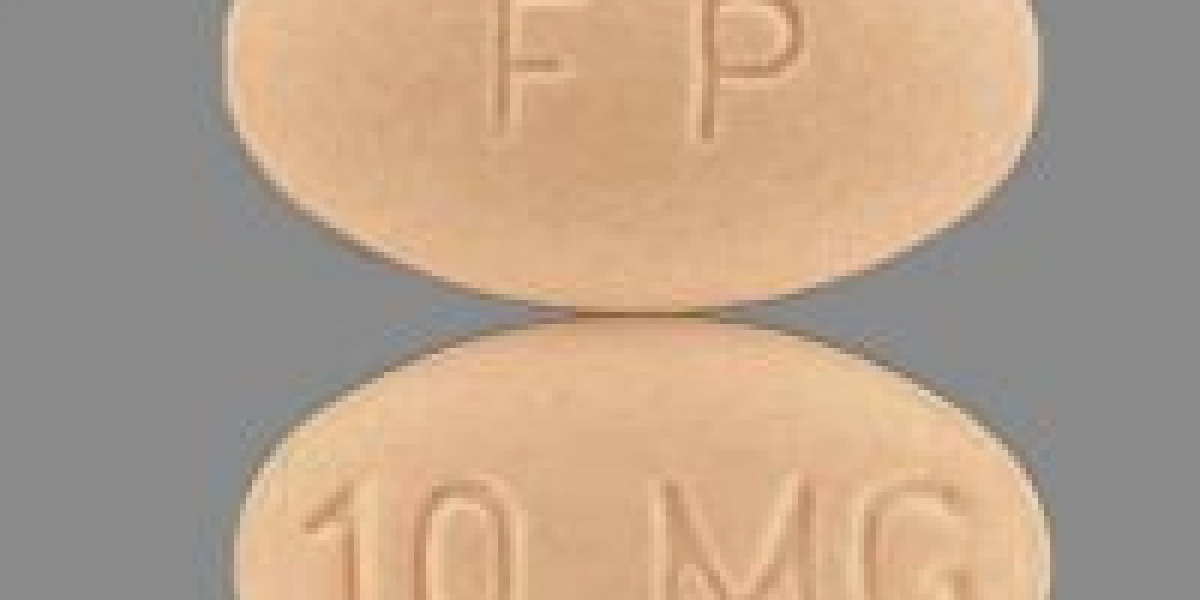
Celexa, or citalopram, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) commonly prescribed to treat depression and anxiety disorders. A unique aspect of Celexa is its relatively lower risk of interacting with other medications compared to some other SSRIs. This feature can make it a more suitable option for individuals who are taking multiple medications for various conditions. Additionally, Celexa has been studied for its potential to improve the quality of life in people with chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia, although it's primarily used for mood disorders. If you're considering starting Celexa, you might explore options to buy Celexa online for convenience and accessibility.
Some dosages are available in different Forms:
What Is Celexa Used For?
Celexa (citalopram) is primarily known as an antidepressant used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD). However, one unique use of Celexa that might not be as widely recognized is its application in managing premature ejaculation. In this context, it's used off-label because its effects on serotonin levels can delay ejaculation, which may help improve sexual performance in some individuals.
How Long For Celexa To Work:
1. Initial Effects:
- First Few Days: You may not notice significant mood changes. Initial side effects like nausea, dizziness, or fatigue might occur.
- Weeks 1-2: Early signs of improvement might be subtle and may not be consistent. Some people might start to feel a slight reduction in anxiety or a bit more energy.
2. Noticeable Improvement:
- Weeks 2-4: Many individuals begin to see a gradual improvement in symptoms of depression. Mood may begin to lift, but full effects are typically not yet felt.
- Weeks 4-6: Most patients experience a more noticeable reduction in depressive symptoms. This is when the therapeutic benefits of Celexa usually become more apparent.
3. Full Effect:
- 6-8 Weeks: The full therapeutic effects of Celexa are generally realized. Significant improvements in mood, anxiety levels, and overall well-being are often observed.
4. Affecting Response Time:
- Individual Variation: Response times can vary. Factors such as age, metabolism, severity of depression, and overall health play a role.
- Dosage: Adjustments may be needed based on your response and tolerance.
- Additional Therapies: Combining Celexa with psychotherapy may enhance overall results and potentially speed up improvement.
5. Tips for Managing Expectations:
- Be Patient: Antidepressants typically require several weeks to show their full effects.
- Consistency: Take Celexa exactly as prescribed and attend regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider.
- Track Progress: Keep a mood journal to help identify changes and discuss them with your doctor.
6. When to Seek Help:
- Lack of Improvement: If you don't notice any improvement within 4-6 weeks, or if symptoms worsen, consult your healthcare provider.
- Severe Side Effects: Report any severe or troubling side effects promptly.
How Long Does It Take For Celexa To Get Out Of Your System?
Celexa's Half-Life:
- For Celexa, the half-life is approximately 35 hours. This means that, theoretically, it takes about 35 hours for the level of Celexa in your blood to decrease by 50%.
- Applying this to Celexa, it would take roughly 175 hours, or about 7 days, for the drug to be cleared from your system. This estimate can vary based on several factors, including your metabolism, liver function, age, and overall health.
- It typically takes about 5 to 6 half-lives for a drug to be eliminated from your system. For Celexa, this translates to approximately 7 to 10 days.
Celexa's Withdrawal Symptoms:
- Electric Shock Sensations: Often described as "brain zaps," these are sudden, brief sensations that can feel like electrical jolts in the head or body.
- Sensory Distortions: Changes in how you perceive sights, sounds, or touch, which might feel unusual or heightened.
- Unusual Dreams: Vivid, bizarre, or distressing dreams that disrupt sleep patterns.
- Coordination Issues: Difficulty with balance or fine motor skills, making tasks that require precision more challenging.
- Emotional Instability: Rapid mood swings or sudden, intense feelings of sadness or anxiety.