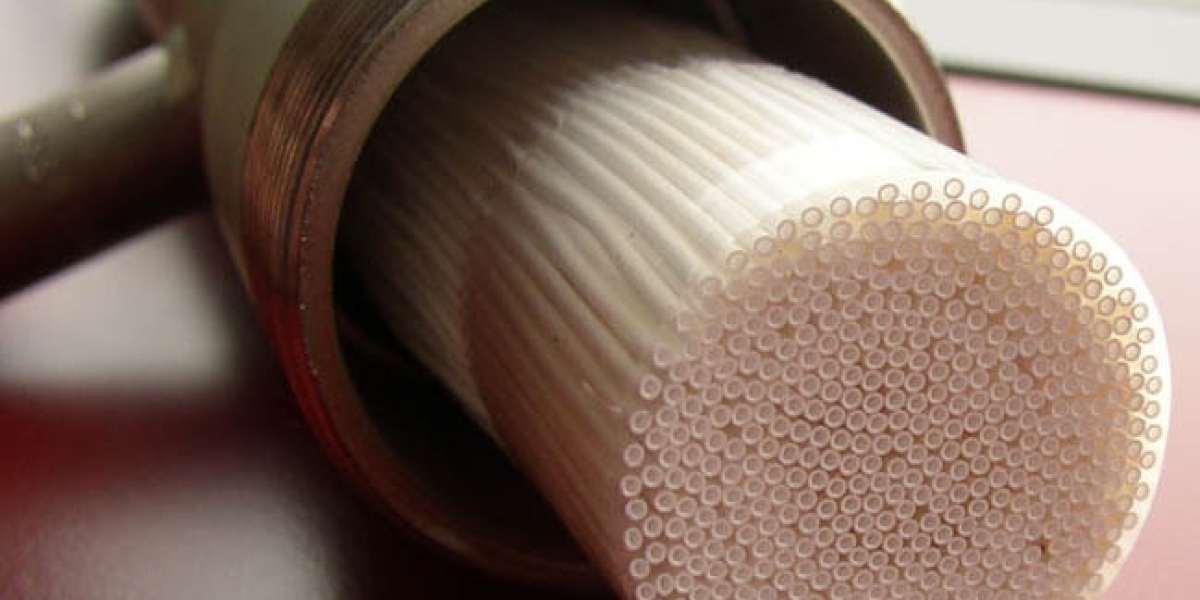
At its core, Hollow Fiber Filtration involves the use of hollow fibers, which are small, tubular membranes with microscopic pores. These fibers act as selective barriers, allowing only certain molecules to pass through while blocking others based on size, shape, and charge.
The Hollow Fiber Filtration process typically occurs within a filtration module or cartridge, where thousands of hollow fibers are bundled together. The liquid to be filtered is passed through the fibers, either inside or outside, depending on the specific configuration of the system. As the liquid flows through the fibers, contaminants are trapped on the surface or within the pores, while clean liquid passes through to the other side.
One of the key advantages of Hollow Fiber Filtration technology is its high surface area-to-volume ratio. Because the filtration occurs within the hollow fibers themselves, rather than on a flat surface, the available surface area for filtration is significantly increased. This allows for greater efficiency and throughput, making Hollow Fiber Filtration ideal for applications where high flow rates and large volumes of liquid need to be processed.
Another important aspect of Hollow Fiber Filtration is its versatility and adaptability to different types of liquids and contaminants. Hollow fibers can be made from a variety of materials, including polymers, ceramics, and metals, each offering unique properties and performance characteristics. This allows for customization of Hollow Fiber Filtration systems to suit specific application requirements, whether it be water treatment, bioprocessing, or industrial filtration.
Get More Insights On This Topic: Hollow Fiber Filtration