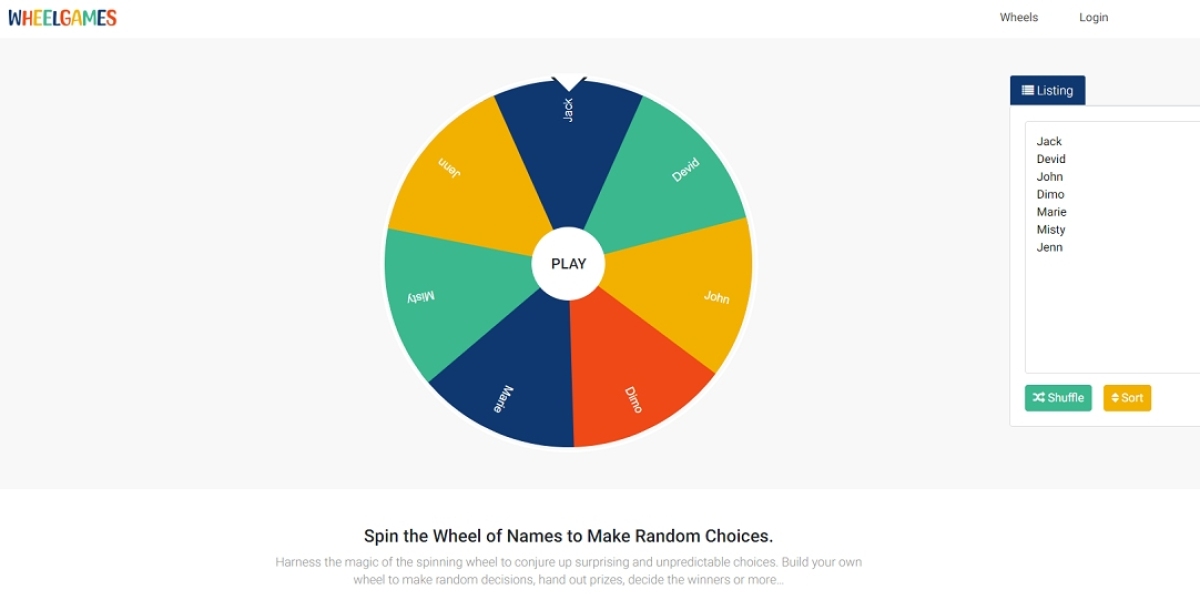
Introduction:
In the world of gambling and games of chance, understanding probability is key to unlocking success. One crucial tool that harnesses the power of probability is the random number generator wheel. These generators, powered by complex algorithms and mathematical principles, play a vital role in creating random outcomes that drive fair and unbiased games. In this article, we delve into the science behind wheel number generators, exploring the concepts of probability, randomness, and the mathematical foundations that make these generators so effective.
The Basics of Probability:
Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood of events occurring. It is expressed as a value between 0 and 1, where 0 represents an impossible event, and 1 represents a certain event. Probability allows us to quantify uncertainty and make informed decisions based on the likelihood of specific outcomes.
Randomness in Probability:
Randomness is a fundamental concept in probability theory. It refers to the lack of predictability or pattern in a sequence of events or outcomes. Randomness ensures that each event is independent and unaffected by previous outcomes, creating a fair and unbiased environment for games of chance. Wheel number generators are designed to generate random outcomes, producing results that are unpredictable and free from any discernible pattern.
Mathematical Algorithms:
Wheel number generators rely on sophisticated mathematical algorithms to generate random numbers. These algorithms utilize complex equations, formulas, and computational techniques to produce sequences of numbers that exhibit the characteristics of randomness. Common algorithms used in wheel number generators include the Mersenne Twister, Linear Congruential Generator (LCG), and XORShift.
Seed Values and Deterministic Algorithms:
Wheel number generators often require a seed value as an input to initiate the generation process. The seed value serves as the starting point for the algorithm, influencing the entire sequence of numbers generated. A crucial point to note is that while the algorithm itself is deterministic, meaning it will always produce the same sequence given the same seed, the choice of seed value is typically unpredictable, ensuring the generation of different sequences each time.
Uniform Distribution:
An essential property of wheel number generators is the production of uniformly distributed numbers. This means that each possible outcome has an equal probability of occurring. For example, in a fair six-sided die roll, each side has a 1/6 probability of landing face up. Wheel number generators strive to achieve this uniform distribution to ensure fairness and eliminate any biases or favoritism.
Testing and Verification:
To ensure the effectiveness and reliability of wheel number generators, they undergo rigorous testing and verification processes. Statistical tests, such as the chi-square test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, and runs test, are employed to assess the randomness and uniformity of the generated sequences. Independent testing laboratories and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in evaluating the performance of wheel number generators and certifying their fairness.
Limitations and Challenges:
While wheel number generators are designed to be highly random and unbiased, they are not without limitations and challenges. Some factors to consider include:
Pseudo-Randomness: Wheel number generators that use deterministic algorithms are technically referred to as pseudo-random number generators (PRNGs). While they offer highly unpredictable sequences, they are not truly random in the mathematical sense. True random number generators (TRNGs) that rely on physical processes provide a higher level of randomness.
Statistical Patterns: Even with rigorous testing, it is still possible for wheel number generators to exhibit statistical patterns that may be exploited. Researchers continually develop new testing methodologies and algorithms to detect and eliminate any patterns or biases that may compromise the integrity of the generator.
Seed Vulnerability: The seed value used to initialize the generator can potentially be vulnerable to manipulation or prediction. Careful implementation and management of seed values are necessary to ensure the security and fairness of the generator.
Randomness and Determinism:
While wheel number generators are designed to produce random outcomes, it is important to note that they are based on deterministic algorithms. Determinism refers to the property that given the same input (seed value), the algorithm will always produce the same output (sequence of numbers). However, the choice of the seed value is typically unpredictable, ensuring that different sequences are generated each time. This combination of determinism and unpredictability creates the appearance of randomness.
Entropy Sources:
To generate truly random numbers, some wheel number generators use entropy sources as an additional input. Entropy sources gather data from various unpredictable physical phenomena, such as atmospheric noise, radioactive decay, or mouse movements. These sources provide a level of randomness that goes beyond the mathematical algorithms alone, enhancing the overall randomness of the generated numbers.
Conclusion:
Wheel number generators are powerful tools that harness the science of probability to generate fair and random outcomes in games of chance. The mathematical algorithms, uniform distribution, and rigorous testing ensure the reliability and effectiveness of these generators. By understanding the science behind wheel number generators, we can appreciate the intricate balance between randomness and predictability, ultimately enhancing our understanding and mastery of probability in the realm of gambling and games of chance.