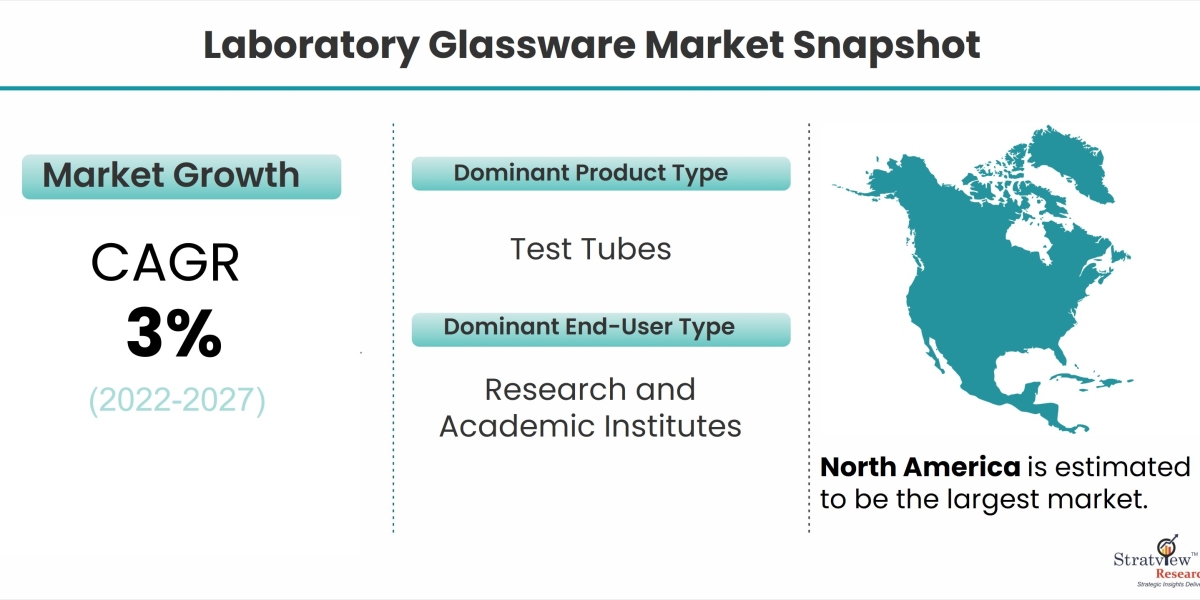
According to Stratview Research, the laboratory glassware market is segmented by Product Type (Beakers, Pipettes, Burettes, Measuring Cylinders, Stirrers, Test Tubes, Watch Glasses, Funnels, Flasks, and Others), by End-User Type (Research and Academic Institutes, Hospitals, and Diagnostic Centers, Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Industry, Contract Research Organizations, Food, and Beverage Industry, and Others), and by Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World).
Laboratory glassware is the unsung hero of scientific research. From beakers and test tubes to pipettes and flasks, the right choice of glassware can significantly impact the accuracy, reliability, and safety of experiments. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of selecting the right laboratory glassware to ensure that your experiments yield the best possible results.
Understand Your Experimental Needs
Before you start shopping for laboratory glassware, it's crucial to have a clear understanding of your experimental requirements. Consider the following factors:
a. Experiment Type: Are you conducting chemical reactions, measurements, or biological assays? Each type of experiment may require different types of glassware.
b. Volume and Precision: Determine the volume range you'll be working with and the level of precision required. Some experiments demand high-precision glassware, while others can tolerate slight variations.
c. Chemical Compatibility: Identify the chemicals you'll be working with. Certain chemicals may react with or corrode specific types of glassware, so it's essential to choose materials that are chemically compatible.
Types of Laboratory Glassware
There is a wide variety of laboratory glassware available, each designed for specific purposes. Here are some common types:
a. Beakers: These are versatile containers for holding, mixing, and heating liquids. They come in various sizes and are ideal for general-purpose use.
b. Flasks: Erlenmeyer flasks, round-bottom flasks, and volumetric flasks are used for mixing, storing, and measuring liquids. They come in various shapes and sizes.
c. Test Tubes: Test tubes are used for small-scale reactions, heating, and observation. They come in different lengths and can be open-ended or closed.
d. Pipettes: Pipettes are used for precise measurement and transfer of liquids. They are available in various types, including volumetric, serological, and micropipettes.
e. Burettes: Burettes are used for precise measurement of liquids during titrations and other analytical procedures.
Material Matters
Laboratory glassware can be made from various materials, including borosilicate glass, quartz glass, and plastic. The choice of material depends on your experiment's requirements:
a. Borosilicate Glass: This is the most common material and is known for its resistance to heat and chemical corrosion. It's suitable for most laboratory applications.
b. Quartz Glass: Quartz glass is highly resistant to high temperatures and is often used in specialized applications where borosilicate glass may not be suitable.
c. Plastic: Plastic laboratory ware is lightweight and cost-effective. It's a good choice for non-corrosive and non-thermal applications.
Quality and Calibration
When choosing laboratory glassware, opt for high-quality, calibrated items. Calibrated glassware is marked with precise volume measurements, ensuring accurate results. Check for quality certifications and calibration standards to ensure reliability.
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a top priority in the laboratory. Ensure that your chosen glassware is designed for the intended purpose and can withstand the conditions of your experiments. Handle glassware carefully to prevent accidents and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care of laboratory glassware are essential for longevity and accuracy. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning, sterilizing, and storing your glassware. Regular inspections can help identify wear and damage that may affect performance.
Conclusion
Selecting the right laboratory glassware is a critical step in ensuring the success of your experiments. By understanding your experimental needs, choosing the appropriate types and materials, prioritizing quality and safety, and maintaining your glassware properly, you can optimize your laboratory processes and achieve more accurate and reliable results in your scientific endeavors.