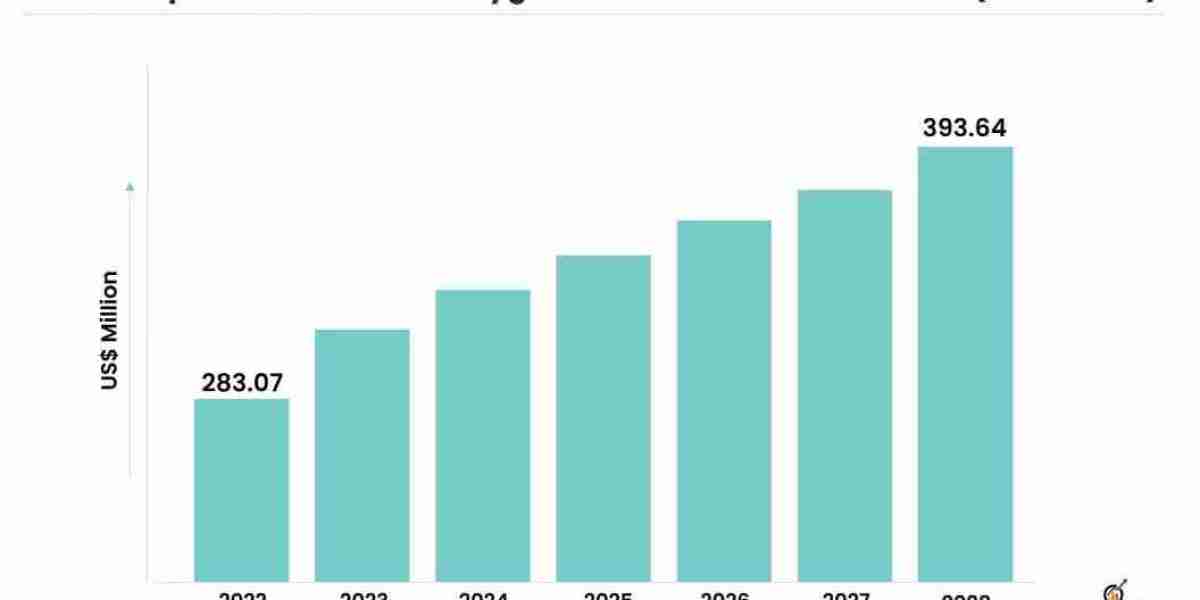
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machines have emerged as a transformative technology in critical care medicine, providing life-saving support to patients with severe cardiac and respiratory failure. Despite their numerous benefits, the adoption of ECMO machines faces various challenges that hinder their widespread use. This article aims to shed light on some of these challenges and explore potential solutions to overcome them. The extracorporeal membrane oxygenation machine market is estimated to grow from USD 283.07 million in 2022 to USD 393.64 million by 2028 at a healthy CAGR of 5.60% during the forecast period.
One of the primary challenges in the adoption of ECMO machines is the high cost associated with their implementation. ECMO treatment requires specialized equipment, skilled healthcare professionals, and continuous monitoring, all of which contribute to the substantial financial burden on healthcare facilities. Additionally, the need for frequent maintenance and replacement of consumables adds to the overall cost. To address this challenge, it is essential to explore cost-effective alternatives and develop strategies to optimize the utilization of ECMO resources without compromising patient care. Collaborations between healthcare institutions and manufacturers can lead to the development of affordable ECMO solutions tailored to specific settings and patient populations.
Another significant hurdle is the complexity of ECMO technology, which requires a highly skilled and specialized workforce. The successful implementation and management of ECMO treatment demand expertise in various disciplines, including critical care medicine, perfusion, and respiratory therapy. Training healthcare professionals to operate ECMO machines effectively and safely is crucial. Establishing comprehensive training programs and certification courses can ensure that medical teams acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to provide optimal ECMO care. Additionally, fostering collaboration between ECMO centers and sharing best practices can facilitate the dissemination of knowledge and enhance the standardization of ECMO protocols.
Infrastructure limitations also pose a challenge to the adoption of ECMO machines, particularly in resource-constrained healthcare settings. ECMO treatment requires dedicated facilities with adequate space, specialized equipment, and robust support systems. However, not all hospitals and clinics have the resources or infrastructure to establish ECMO programs. Overcoming this challenge necessitates a multi-faceted approach. Governments and healthcare organizations can allocate resources to develop regional ECMO centers that serve a broader population. Collaboration between institutions can facilitate the sharing of ECMO resources and expertise, allowing for more efficient utilization of available infrastructure. Furthermore, technological advancements in ECMO equipment, such as the development of compact and portable devices, can enhance accessibility and enable ECMO treatment in a wider range of healthcare settings.
Regulatory considerations also play a significant role in the adoption of ECMO machines. The approval and licensing processes for ECMO equipment can be lengthy and cumbersome, often resulting in delays in their availability. Streamlining and expediting the regulatory pathways for ECMO machines, while maintaining stringent safety standards, is crucial. Regulatory authorities should work closely with manufacturers to ensure a robust yet efficient approval process that facilitates the timely introduction of ECMO technology into the market.
Additionally, raising awareness and understanding of ECMO among healthcare providers and the general public is essential. Educating clinicians about the indications, benefits, and potential risks of ECMO treatment can encourage its appropriate and timely use. Public awareness campaigns and patient advocacy groups can help disseminate information about ECMO, ensuring that patients and their families are aware of this life-saving option.
In conclusion, while extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machines offer immense potential in critical care medicine, several challenges hinder their widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach involving healthcare institutions, manufacturers, regulatory authorities, and policymakers. By focusing on cost-effective solutions, specialized training, infrastructure development, streamlined regulations, and raising awareness, it is possible to overcome these challenges and foster the wider adoption of ECMO machines. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to improved patient outcomes and a brighter future for critical care medicine.