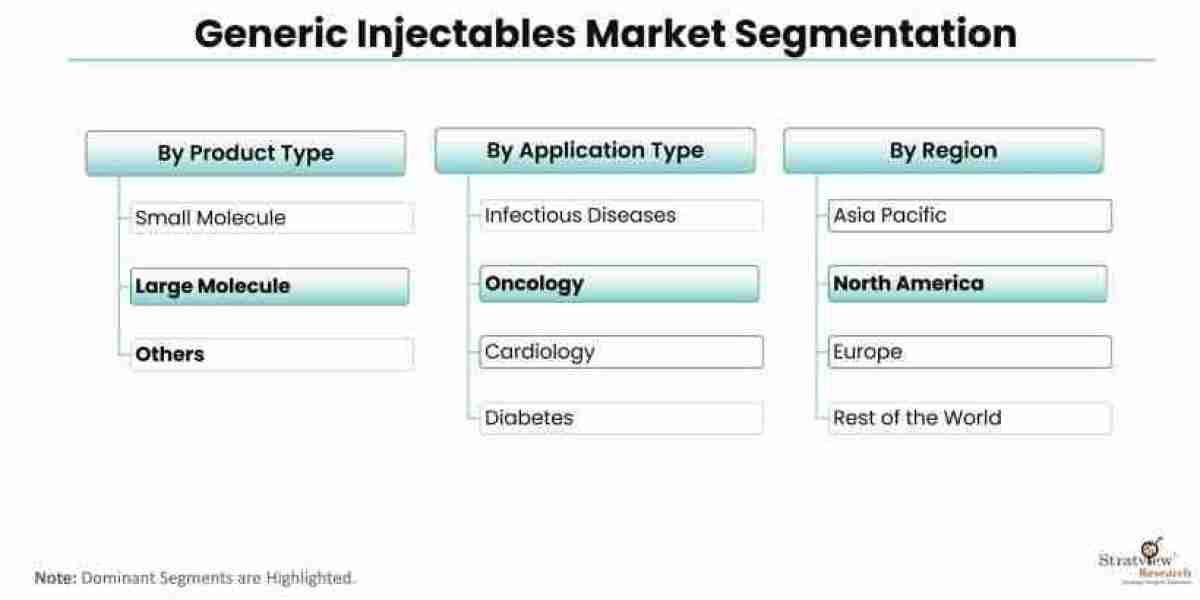
The regulatory landscape for generic injectables plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of these medications. The process of bringing generic injectables to market involves navigating complex regulatory frameworks and complying with stringent requirements. While the regulatory environment presents challenges for manufacturers, it also offers opportunities for growth and market differentiation. This article provides an overview of the regulatory landscape for generic injectables, highlighting the challenges faced by manufacturers and the opportunities for success. The generic injectables market is estimated to grow from USD 122.4 billion in 2022 to USD 250.13 billion by 2028 at a healthy CAGR of 12.60% during the forecast period.
Challenges in the Regulatory Landscape:
Bioequivalence Studies: Generic injectables must demonstrate bioequivalence to the reference brand-name product. Conducting bioequivalence studies involves comparing the pharmacokinetic properties of the generic drug with those of the reference drug. This process requires rigorous testing and analysis to establish the therapeutic equivalence of the generic injectable. The complexity and cost associated with bioequivalence studies pose a significant challenge for manufacturers.
Stringent Quality and Safety Standards: Regulatory authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), impose stringent quality and safety standards for generic injectables. Manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality. Compliance with these standards necessitates robust quality control systems, regular inspections, and continuous monitoring of manufacturing processes. Meeting these requirements can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
Patent and Intellectual Property Issues: The generic injectables market often faces challenges related to patents and intellectual property rights. Manufacturers must navigate patent landscapes, considering the scope of existing patents and potential litigation risks. Ensuring compliance with intellectual property regulations is crucial to avoid legal disputes and delays in market entry.
Complex Regulatory Submissions: Submitting regulatory dossiers for generic injectables requires comprehensive data and documentation. Manufacturers must provide detailed information on the drug's quality, safety, and efficacy, along with analytical and stability data. Preparing these submissions demands expertise in regulatory affairs and a thorough understanding of regional requirements. The complexity of these submissions can pose challenges, particularly for small and medium-sized manufacturers.
Opportunities in the Regulatory Landscape:
Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDAs): Generic injectable manufacturers can leverage the Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) pathway to gain regulatory approval. ANDAs allow manufacturers to demonstrate bioequivalence to the reference product, streamlining the approval process. By obtaining regulatory clearance through ANDAs, manufacturers can enter the market faster and benefit from the market exclusivity period.
Regulatory Exclusivity: In some cases, generic injectable manufacturers can obtain regulatory exclusivity for their products. This exclusivity period grants them market exclusivity for a specified duration, preventing the entry of competing generic versions. Regulatory exclusivity provides an opportunity for manufacturers to capture a significant market share and establish their products as preferred alternatives.
Global Harmonization Initiatives: Regulatory authorities worldwide are increasingly working towards harmonizing regulatory standards and processes. Initiatives like the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) aim to promote uniformity in regulatory requirements across regions. Such harmonization efforts can streamline the regulatory process, facilitate global market access, and reduce the burden on manufacturers.
Pharmacovigilance and Post-Market Surveillance: Ensuring the safety and efficacy of generic injectables extends beyond regulatory approval. Manufacturers have the opportunity to establish robust pharmacovigilance systems and post-market surveillance programs. By actively monitoring the safety and effectiveness of their products, manufacturers can enhance patient trust, differentiate themselves in the market, and identify opportunities for product improvement.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for generic injectables presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. Compliance with stringent quality and safety standards, conducting bioequivalence studies, and navigating patent and intellectual property issues are among the challenges faced by manufacturers. However, opportunities arise through streamlined regulatory pathways like ANDAs, regulatory exclusivity, global harmonization initiatives, and post-market surveillance programs. By effectively navigating the regulatory landscape, manufacturers can gain regulatory approval, differentiate themselves in the market, and contribute to providing accessible and affordable healthcare solutions to patients worldwide.