Agile testing is a continuous testing process which is iterative in nature and aligns itself with Agile Development Methodology.
The Agile development model is iterative and incremental. Agile approach in Software Development revolves around collaboration, transparency, flexibility and responsiveness to feedback throughout the software development lifecycle.
Agile Testing is a continuous testing approach spanning all the phases of development until the delivery to the end customer.
Core Principles/Values of Agile Testing
- Testing is Continuous and not just a phase : Testing is not phased at the end, but is done throughout the project development life cycle.
- Testing is a collective responsibility : Traditionally, testing was done by a team of Quality Assurance individuals. But in Agile approach, everyone i.e. developers, analysts, QA team is involved in testing from the very onset of the project as one agile team.
- Development approach is test driven : In Agile testing process, the test cases are written along with customer requirements analysis. (A popular form of agile requirements is the story, which conventionally includes acceptance tests.) This ensures that the tests are aligned with the end goals. Hence, the development process is actually test driven.
- Focus on people and their interactions : This principle implies that there has been a paradigm shift from stringent processes to flexible approach which encourages free communication flow between teams. It means that agile testing can leverage tools and processes as much as possible, but positive outcomes will happen only when there is communication between the teams regarding test results and fixing them as soon as they are discovered.
- Feedback is continuous : Agile testing process makes sure that there is a continuous feedback loop for bug reporting and fixing, and even requirements and plan changes. For example, if a story has too many defects to fix in the current sprint, it can be pulled and deferred to the next, or another comparable in effort story or set may be pulled if they are lower in priority.
- Improved Collaboration with Customers : Frequent interaction and collaboration helps in establishing better understanding between the working team and the customer. It also aid in checking whether the progress of work is in sync with the delivery (e.g. sprint or iteration) plan.
- Focus on stable and working software at every rollout point : The aim of agile testing is to ensure that a functional and usable software is ready after every iteration. Continuous testing, feedback and bug fixing cycle plays an important role in this.
- Keep the Code clean : The defects are fixed as soon as they are reported. This is done within the current iteration instead of delayed fixing. This ensures that quality is maintained.
- Responding to change : A disposition towards embracing change is the key for implementing agile testing process. Testing process and plan are defined keeping in mind certain requirements. There should be a provision and flexibility to implement any change request raised by customer or process.
- Easy to manage Documentation : Documentation is important, but the key is to document the right things. Agile methodology encourages usage of reusable test plans and checklists which can be shared across the development and QA teams.
Agile Testing Quadrants
Developers/Testers need to have clarity about end goals of testing for designing a good test plan.
Tests could be either Business facing or Technology facing. As the name suggests, Business facing tests are designed to address the business needs. Technology facing tests are designed within the gamut of technological domain.
Another aspect to consider is whether the test is supporting the team in product development or it is aiding in product verification.
These relationships can be explained with the help of Agile Testing Quadrants.
Agile Testing Quadrants aid in understanding the relationship between various types of tests which help the team address the business and technological needs by employing stringent testing approach, both manual and automated, at different phases.
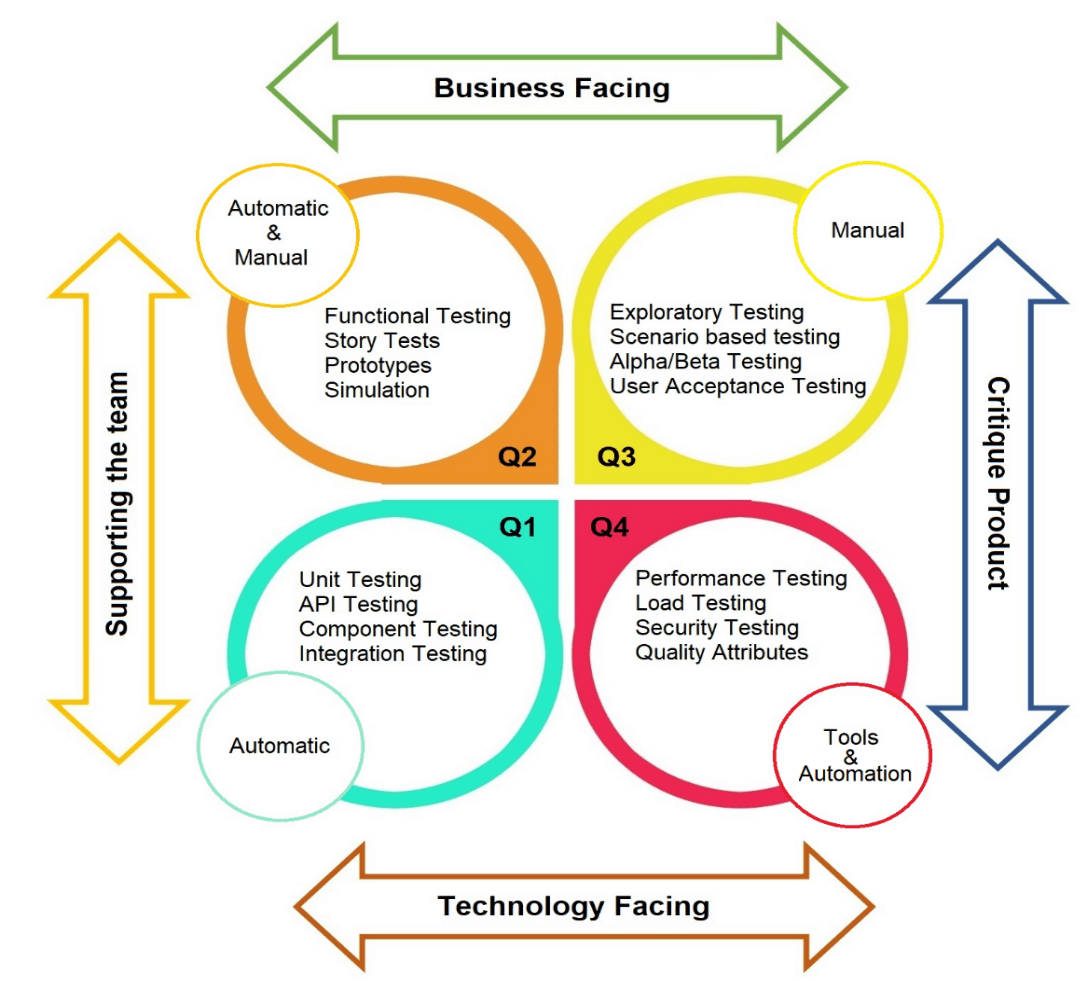
Quadrant 1
This quadrant supports the team in developing and executing technology facing tests which results in high quality of code. The tests performed in this quadrant can be automated.
Quadrant 2
This quadrant supports the team in developing and executing business facing tests keeping business objectives in mind. This involves interactions between developer/tester and business stakeholders on a continuous basis. The tests performed in this quadrant can be either manual or automated.
Webomates CI/CD service allows the agile teams to do regression testing as a part of each build.
Quadrant 3
This quadrant provides feedback to Quadrant 1 and 2. The iterative tests performed in this quadrant verifies business needs with stringent testing. The tests performed in this quadrant are manual.
Quadrant 4
This quadrant focuses on non-functional requirements like security, stability, performance, scalability, maintainability etc. Special tools are employed to perform these tests. Some tests are also done using automation scripts.
Agile Testing Methodologies
Agile testing methodologies assist the teams in extracting maximum benefits for precise results.

- Test Driven Development : This methodology focuses on unit tests. The developer writes unit test cases to address a specific requirement. The code is then written for those test cases. This fundamentally differs from traditional programming practice where developers write test cases after the code was written. The code should pass all the test cases for a specific requirement.
- Behaviour Driven Development : Behaviour Driven Development calls for higher level tests at business level equating to specific business goals. It encourages free flow of communication between project stakeholders, i.e. developer, tester and customer, for a better understanding of the functionality of each feature.Behaviour Driven Testing employs easy to understand language which non-technical people on team can also understand. This encourages better collaboration between analysts, customers and technical team.
- Acceptance Test Driven Development (ATDD) : Acceptance Test Driven Development focuses on how the end user will actually use a particular feature. It encourages interaction between end user, developer and tester to understand User acceptance criteria. User acceptance tests are written by the team keeping user’s point of view in mind. These test cases for the point of reference for development.
- Exploratory Testing : As the name suggests, Instead of following predefined test cases, the testers “explore” the working software and record the findings. It is based on learn-on-the-go technique. The testers learn about the functionality of a software and then design and execute test cases based on their learning. Essentially, test design and test execution phase are done simultaneously. Exploratory testing aims to find hidden bugs and risks.
- Session Based Testing : Session based testing builds on Exploratory Testing by rendering it a structured format. Session based testing needs to have a testing charter stating what needs to be tested. Testing is done in time based session. The results of testing performed in that session have to be recorded and then discussed with developer and manager. It adds accountability dimension to Exploratory Testing.Read for more about :https://www.webomates.com/blog/agile-testing/agile-testing/