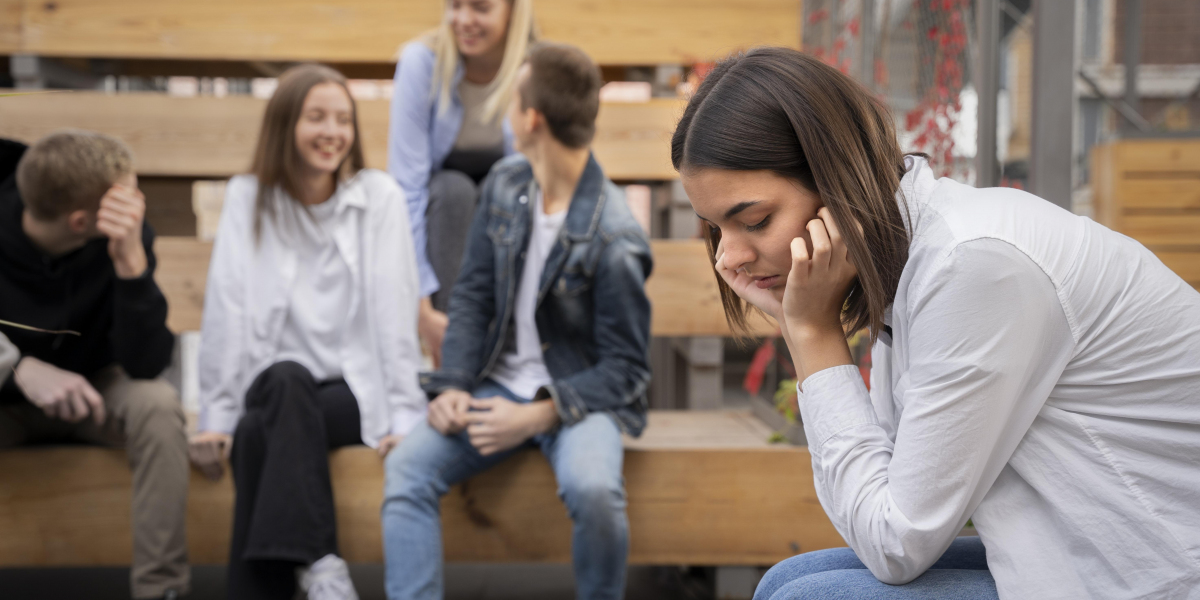
Youth mental health has reached a crucial juncture, with experts around the world warning of the seriousness of the situation. A world-renowned study has called youth mental health a global crisis, highlighting an increasing amount of mental health illnesses among young people.
These difficulties are no longer limited to specific regions or communities; they now affect millions of youths worldwide. As our youth's mental health worsens, it becomes increasingly evident that tackling this issue is critical not only for individual well-being but also for society's long-term health.
Understanding the Global Crisis
The youth mental health crisis refers to the rapid increase in mental health issues among adolescents and young adults, such as anxiety, depression, self-harm, and suicide.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified mental health disorders as one of the leading causes of illness and disability among youth aged 10 to 19.
As young people grapple with growing social, economic, and environmental pressures, the emotional toll is evident in the rising rates of mental illness.
Factors contributing to the growing crisis
Several factors contribute to the youth mental health crisis:
- Social Media: The rise of social media has increased feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, and isolation among young people, with many comparing their lives to unrealistic standards portrayed online.
- Academic Pressure: Increasing academic demands and pressure to succeed often contribute to heightened stress and mental health challenges.
- Pandemics and Political Instability: Events like the COVID-19 pandemic and political unrest have exacerbated mental health issues, leaving young people more vulnerable to stress, uncertainty, and fear for their future.
Key Findings from the World-Leading Study
The global study on youth mental health highlights several concerning trends. Among its most significant findings are:
- Rising Rates of Mental Health Disorders: The study reveals that one in five youth now suffers from a mental health disorder, including anxiety, depression, and behavioral disorders. These numbers have surged in the last decade, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Geographical Patterns: While mental health challenges are prevalent worldwide, certain regions face more acute crises. For example, high-income countries report rising rates of depression and anxiety among youth, while in lower-income nations, the lack of resources exacerbates untreated mental health conditions.
- Socio-Economic Disparities: The study also notes a strong link between socio-economic status and mental health. Youths from poorer backgrounds are more likely to face significant mental health challenges due to increased exposure to violence, financial instability, and lack of access to healthcare and education.
Impact of the Crisis on Young People
The youth mental health crisis has profound implications for the emotional, social, and academic development of young people.
- Emotional and Psychological Development: Mental health plays a critical role in a young person’s ability to manage emotions and navigate challenges. Poor mental health can disrupt emotional growth, leading to struggles in coping with stress and forming a healthy self-identity. Over time, untreated mental health issues can cause long-lasting emotional scars, leading to chronic stress, low self-esteem, and difficulties in personal relationships.
- Academic Performance: Mental health issues often hinder academic performance. Anxiety and depression can affect concentration, motivation, and the ability to retain information, which in turn leads to lower grades and disengagement from school. In severe cases, mental health challenges can result in absenteeism, school dropout, or an inability to pursue higher education and career opportunities.
- Social Interactions: Adolescents with mental health issues may struggle to form and maintain meaningful relationships. Social anxiety, low self-worth, and depression can lead to withdrawal from peers, contributing to loneliness and isolation. Over time, these social difficulties can snowball, creating further emotional distress and reinforcing negative mental health cycles.
Consequences of Poor Mental Health
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects:
Poor mental health has both immediate and long-term consequences for young people. In the short term, it can lead to academic failure, substance abuse, and strained relationships with family and peers.
In the long term, untreated mental health conditions can escalate into chronic mental illness, substance dependency, unemployment, and increased risk of suicide.
Potential Risks and Challenges:
Adolescents facing mental health challenges are at greater risk of engaging in dangerous behaviors such as self-harm, risky sexual behavior, and substance abuse.
These behaviors often serve as coping mechanisms for the emotional pain and distress young people experience, but they also present additional dangers that can lead to physical harm and even death.
Importance of Early Intervention
Benefits of Addressing Mental Health Issues Early:
Early intervention is crucial in mitigating the effects of mental health disorders. Addressing mental health concerns at their onset can prevent them from worsening and improve the overall quality of life for young people.
With timely support, young people can develop healthy coping strategies, improve resilience, and return to a path of emotional and psychological well-being.
Strategies for Early Detection and Intervention:
Schools, families, and communities play a vital role in early detection. Teachers and parents should be aware of behavioral changes such as withdrawal from social activities, a drop in academic performance, or mood swings.
Mental health screenings in schools and youth programs can also identify early signs of mental health problems, allowing for timely intervention.
Role of Families and Caregivers
How Family Support Can Positively Impact Mental Health?
Family plays an essential role in a young person’s mental health. A supportive and understanding family environment can help adolescents navigate mental health challenges, reduce feelings of isolation, and foster a sense of security.
Open communication, empathy, and active listening from parents and caregivers are vital in promoting mental well-being.
Effective Communication and Support Strategies
Parents and caregivers should encourage open dialogue about mental health, reducing the stigma that often surrounds these conversations.
By showing empathy and avoiding judgment, families can create a safe space for young people to express their emotions and seek help when needed.
Community and School Contributions
- Role of Schools in Promoting Mental Health: Schools are essential in addressing the youth mental health crisis. Counseling services, mental health education, and school-based interventions can provide vital support for students.
Schools can also promote mental well-being by fostering a positive and inclusive environment, encouraging peer support, and training staff to recognize mental health concerns. - Community Resources and Support Systems: Communities offer additional resources for addressing mental health. Youth centers, mental health organizations, and local support groups can provide essential services for young people who may not have access to school-based support. Community initiatives that focus on mental health awareness and advocacy also play a crucial role in reducing stigma and encouraging early intervention.
Steps to Support Youth Mental Health
Encouraging Proactive Approaches to Youth Mental Health
Addressing the youth mental health crisis requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. Governments, schools, healthcare providers, and families must work together to create comprehensive mental health support systems.
Raising awareness, increasing access to mental health services, and reducing the stigma around mental health are critical steps in combating this crisis.
Resources for Further Information and Support
Numerous resources are available to help families, educators, and communities address youth mental health issues. Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), Mental Health America (MHA), and local mental health centers provide guidance, counseling, and support for young people facing mental health challenges.
Final Thoughts
The global youth mental health crisis is a serious and growing concern, with profound implications for the future of millions of young people. By understanding the scope of the crisis, addressing its root causes, and implementing effective interventions, we can work toward a healthier future for our youth. Early detection, family support, and community involvement are essential in ensuring that every young person has the chance to thrive emotionally, socially, and academically. The time to act is now, and together, we can turn the tide on the global youth mental health crisis.