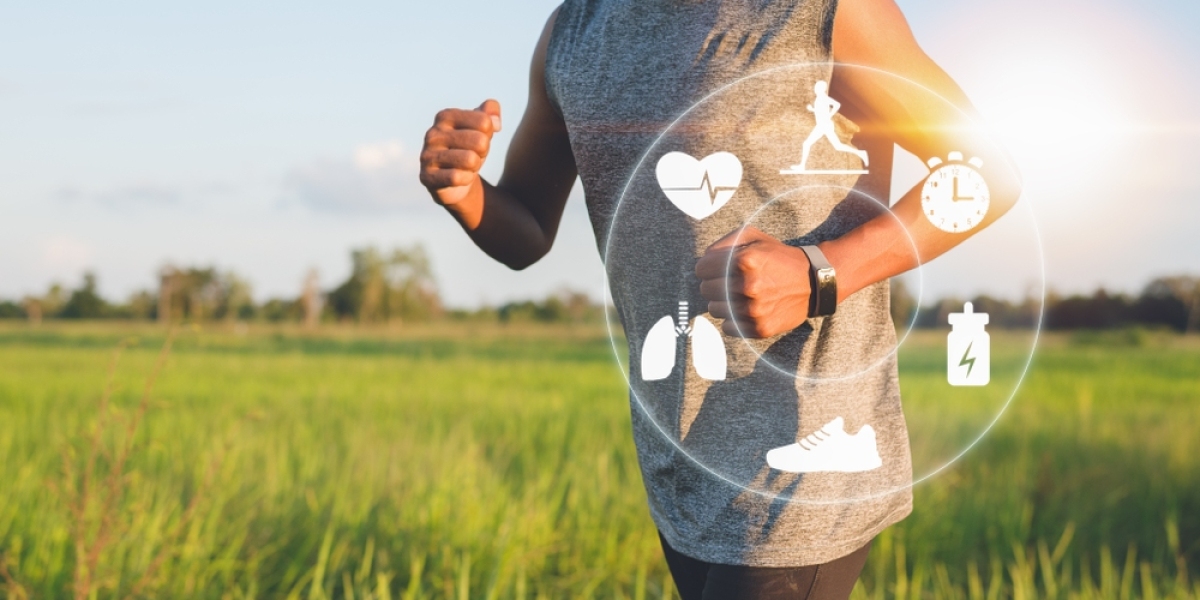
Wearable sensors and devices have seen rapid adoption in consumer markets in recent years. These small, lightweight electronics can be worn on the body and capable of monitoring a wide range of vital health metrics as well as contextual data about physical activity and the surrounding environment. As the capabilities of sensors have advanced, many businesses have started exploring ways to leverage these technologies to gather new insights about employee performance, health, safety and more.
Tracking Productivity and Tasks
One of the most direct applications of sensors at work is to track tasks, duties and productivity levels. Sensor-enabled badges, vests, or wrist-worn devices can monitor an employee's movements, location, and interactions throughout the workday. For jobs involving physical labor or time-sensitive tasks, wearables offer a way to automatically log start and end times as well as duration for each activity. Beyond time tracking, sensors can also capture details about tasks like the number of items handled, distance traveled, repetitions of motions, and more objective metrics of performance. Combined with backend analytics, this detailed task data enables managers to optimize workflows, resource allocation and more accurately measure individual contributions.
Improving Workplace Safety
Workplace safety is a major concern for many businesses, particularly those operating in hazardous conditions or workflows involving heavy machinery. Sensors provide new possibilities for proactively monitoring worker safety. Devices capable of tracking biometric indicators like heart rate, breathing patterns and body temperature can send alerts if signs of distress, overexertion or potential injuries are detected. Location trackers allow easy establishment of restricted zones and geofencing capabilities to prevent access to hazardous areas. Motion and fall detection sensors immediately report any potential accident. Combined with contextual environmental data, wearables create a virtual safety net for remote or lone workers as well. The detailed safety analytics also help identify patterns that can aid in risk mitigation and training improvements over time.
Boosting Employee Health and Wellness
Many employers have begun implementing wellness programs to help workers stay healthy, reduce absenteeism and encourage safe lifestyle habits. Wearable sensors take these efforts a step further by continuously monitoring key employee health metrics. Devices that track activity levels, heart rate variability, sleep patterns and more provide unprecedented insights into real-time wellness as well as long term trends. Personalized dashboards and coaching can then leverage this biometric data to promote improved fitness, healthier routines and earlier intervention for potential health issues. On the job, biometric monitoring through wearables also enables proactive response to signs of stress, fatigue or other issues impacting performance that could be addressed through adjustments to work patterns or additional support. The integration of health tracking elevates wellness initiatives from occasional check-ins to an always-on, personalized approach for each employee.
Enhancing Product and Service Offerings
Beyond internal applications, wearable sensors are finding innovative uses across entire industries to enhance products and services offered to customers. For field service workers, wearables facilitates hands-free access to technical manuals, manuals, inventory and problem diagnostic assistance through augmented reality interfaces. Real-time sensor data from tools and worker biometrics helps monitor equipment utilization and spot issues before major breakdowns occur. Manufacturing and logistics companies use wearables on production lines and in warehouses to guide employees through complex processes and optimize workflows. Sensor-enabled items may tap into Internet of Things platforms to monitor product usage patterns that reveal insights for improving design and service models across the product lifecycle. As technologies like these continue developing symbiotic performance boosts for both workers and customers, companies striving to innovate will find wearables a rich source of new opportunities.
Overcoming Practical and Ethical Challenges
While the potential benefits seem vast, widespread adoption of wearable technology in businesses faces hurdles to overcome. Practical challenges include high upfront and ongoing costs of equipment and analytics, compatibility between diverse devices and systems, as well as user acceptance of wearing monitors constantly at work. On the ethics front, companies must thoughtfully address privacy and data ownership concerns.
In Summary, with myriad sensitive details about employees constantly being collected and analyzed, strong governance policies are required regarding what information is tracked, how and where it is stored, who has access, and employee consent for usage of their personal data. Transparency about how wearable data impacts decisions affecting individuals is also important to build trust over time. As approaches to address these mature challenges, sensors are poised to transform the future of work by empowering new levels of insight, productivity and care for employee well-being.