Understanding the differences between these types of outdoor antennas can help you make an informed decision about which one is best suited to your needs.
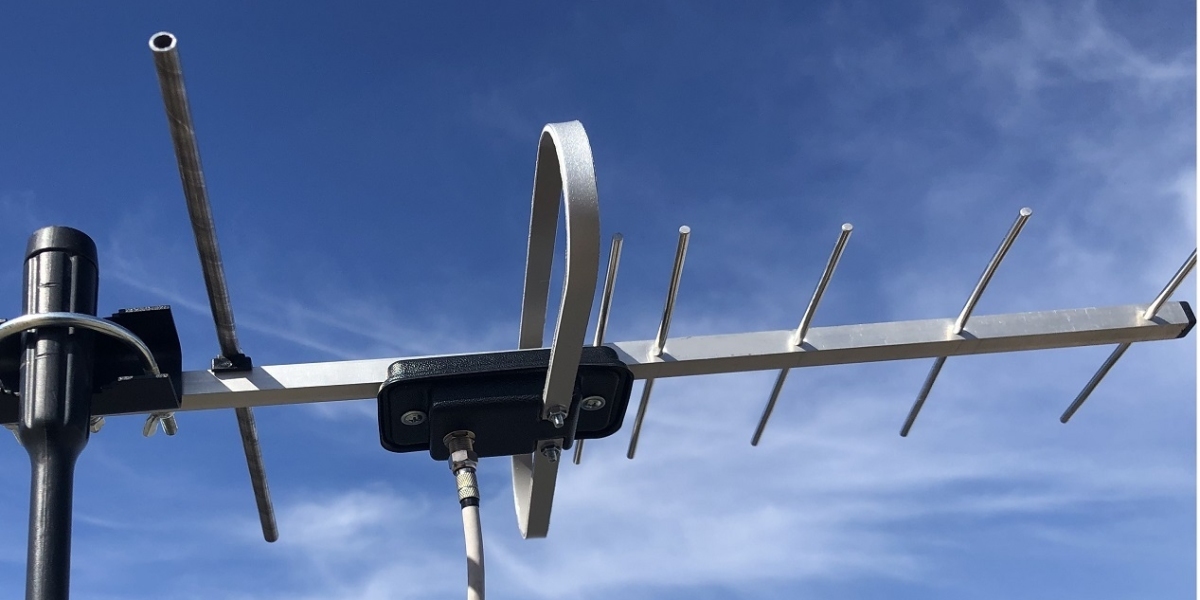
- Yagi Antennas: Yagi antennas are among the most common types of outdoor antennas and are characterized by their long, narrow design with multiple elements arranged in a line. They are directional antennas, meaning they must be pointed in the direction of the broadcast tower to receive signals effectively. Yagi antennas are known for their high gain and long-range reception capabilities, making them ideal for areas with weak signal strength or distant broadcast towers.
- Log-Periodic Antennas: Log-periodic antennas are another popular choice for Outdoor Antenna installations. Unlike Yagi antennas, which have a single directionality, log-periodic antennas have a broader beamwidth, allowing them to receive signals from multiple directions simultaneously. This omnidirectional capability makes log-periodic antennas well-suited for areas with multiple broadcast towers or where signal strength varies.
- Multi-Directional Antennas: Multi-directional antennas are designed to receive signals from multiple directions without the need for precise aiming. They typically feature a compact, square or rectangular design and are ideal for urban or suburban areas where broadcast towers may be located in different directions. Multi-directional antennas offer versatility and ease of installation, making them a popular choice for residential applications.
- Parabolic Grid Antennas: Parabolic grid antennas consist of a grid-shaped reflector dish with a central feed antenna, similar to satellite dishes. They are highly directional antennas with a narrow beamwidth, making them suitable for long-range reception in rural or remote areas. Parabolic grid antennas offer excellent gain and signal focusing capabilities but require precise alignment with the broadcast tower for optimal performance.
Get More Insights On This Topic: Outdoor Antenna